B2B marketing campaigns can quickly become costly experiments rather than strategic investments if performance isn’t measured accurately. Businesses that fail to track results can overspend on ineffective channels, miss opportunities for optimization, and struggle to demonstrate ROI. By adopting advanced measurement models such as Unified Marketing Measurement and leveraging platforms like Lifesight, marketers gain clarity on which campaigns truly drive revenue, engagement, and growth.
In 2025 and beyond, precise measurement is essential for ensuring every marketing dollar delivers tangible business impact and sustainable success.
What is B2B Marketing Measurement?
B2B marketing measurement is the process of tracking and analyzing the effectiveness of business-to-business marketing campaigns and their attributed strategies which helps to drive overall business outcomes like increase in sales, revenue growth and more. The B2B marketing measurement tracking and analyzing process involves measuring campaign spend and evaluating the return on investment (ROI) to understand marketing effectiveness.
Read About: Content Marketing Measurement, Digital Marketing Measurement, B2B Marketing Measurement
Why Measuring B2B Marketing Campaigns is Essential in 2025?
Measuring B2B marketing is essential for effective budget allocation, campaign optimization, justifying marketing spend, eliminating guesswork, and making data-driven decisions.
Here are the Key Reasons to Measure B2B Marketing Campaigns:
1. Budget Allocation
In a world where marketing budgets are often under scrutiny, having data-backed insights into campaign performance is vital for justifying the allocation of resources. Without measurement, businesses risk overspending on underperforming channels or neglecting high-performing ones. Measurement gives clarity, ensuring resources are allocated where they will have the most significant impact.
Effective budget allocation ensures that marketing resources are directed to the right channels and campaigns that yield the highest return on investment (ROI). By measuring the performance of each campaign, businesses can identify which tactics and channels are most effective in reaching their target audience. This helps marketers allocate funds more efficiently, avoiding wasteful spending and ensuring that every dollar is spent in the most impactful way.
2. Optimizing the Marketing Campaigns
B2B marketing campaigns aren’t static, they need constant refinement. With the insights gained through measuring campaign results, businesses can make adjustments to optimize performance. Optimization might involve A/B testing, re-targeting ads, or shifting focus to higher-performing content or channels. Regular analysis and iteration ensure that marketing campaigns are always evolving and improving.
Measuring campaigns allows for continuous improvement. By tracking metrics like click-through rates, conversion rates, and customer engagement, businesses can quickly identify what’s working and what’s not. This enables real-time adjustments, such as tweaking ad creatives, adjusting targeting, or revising messaging to enhance performance.
3. Justifying the Marketing Spend
Businesses face greater pressure to demonstrate the ROI of their marketing efforts. Detailed measurement allows marketers to show how their campaigns are directly contributing to lead generation, customer acquisition, and sales. Without measurable results, marketing departments may struggle to secure funding for future campaigns, or worse, face cuts in their budgets. Data-backed results build credibility and ensure continued investment in marketing.
In 2025, marketing budgets are increasingly tied to measurable outcomes. Senior executives and stakeholders expect concrete data that proves marketing investments are driving revenue and growth. By measuring campaign performance, marketing teams can provide clear evidence of their contribution to business success, making it easier to justify their budgets for future campaigns.
4. Eliminating the Guesswork and Making Data-Driven Decisions
Guesswork in marketing can lead to wasted efforts, missed opportunities, and poor outcomes. By relying on data-driven insights, businesses can avoid the pitfalls of making decisions based on assumptions or past experiences alone. With clear metrics, teams can be more strategic, targeting the right audience with the right messaging at the right time. Data-driven decision-making not only optimizes marketing strategies but also fosters confidence among stakeholders and investors.
In the past, marketing strategies often relied on gut feeling and intuition. But in 2025, decision-making must be based on facts, data, and analytics. By measuring B2B marketing campaigns, businesses can eliminate guesswork and make decisions backed by reliable data. This helps marketers make more accurate forecasts, identify market trends, and adopt strategies that are most likely to succeed.
Why Measuring B2B Marketing ROI is Challenging?
Measuring B2B marketing ROI is challenging due to several factors, including the complexity of tracking attribution, long and complicated sales cycles, intricate buyer journeys, and managing goals across multiple siloed tools. These challenges require more advanced approaches and tools to gain accurate insights into marketing effectiveness.
Here’s the key challenges in measuring B2B marketing ROI explained in detail below:
1. Difficulty in Tracking Attribution
Attribution in B2B marketing is complex due to multiple touchpoints and interactions a buyer has before making a purchase decision. In today’s world of growing social media channels and content marketing platforms, understanding which specific touchpoint or channel is responsible for a conversion is no longer straightforward.
B2B buyers engage with a variety of channels, such as social media, emails, content, and paid ads, before making a final decision. Multi-touch attribution is a model that attempts to give credit to every touchpoint a customer encounters along their journey. However, accurately assigning the right amount of credit to each interaction becomes difficult as buyers are increasingly exposed to various marketing tactics across different platforms. Without a clear attribution model, businesses risk misjudging the impact of each channel and making inefficient budget decisions. Advanced attribution models are necessary to fully understand the performance of marketing efforts across multiple touchpoints.
2. Complex Buyer Journeys
In B2B marketing, the buyer journey is multi-layered, involving several stages, multiple stakeholders, and various decision-making processes. This complexity makes it difficult to track and attribute success to specific actions or touchpoints along the way.
Unlike B2C, where the path to purchase is often shorter and simpler, B2B buyers typically engage in a more complex journey. They may conduct extensive research, consult with colleagues, attend webinars, or request product demos, and evaluate multiple vendors before making a final purchasing decision. As a result, tracking this multifaceted journey is a challenge for marketers, as it’s hard to determine which specific marketing touchpoint or content piece contributed most to the sale. Without understanding the complete buyer journey, businesses may overlook the influence of certain touchpoints and fail to optimize their strategies accordingly.
3. Long and Complex Sales Cycles
B2B sales cycles often span months or even years, which can delay the ability to measure immediate ROI from marketing efforts. The long time between initial contact and conversion complicates tracking how marketing initiatives directly contribute to final sales outcomes.
In B2B marketing, sales cycles tend to be lengthier due to the size and complexity of the deals involved. Marketers often have to wait months before they see the results of their efforts in terms of actual sales, making it hard to link campaigns with immediate returns. In addition, multiple touchpoints are involved in closing a deal, with numerous stakeholders having their input on the final decision. This extended cycle creates a gap in measuring ROI, requiring businesses to adopt long-term tracking mechanisms that can attribute marketing efforts to eventual conversions.
4. Tracking Goals Using Multiple Siloed Tools
Many B2B marketing teams rely on several platforms to manage campaigns, such as email marketing, CRM systems, social media analytics, and ad platforms. These tools often operate in silos and are biased toward last-click attribution, which gives disproportionate credit to the final touchpoint rather than the entire buyer journey.
Siloed tools create fragmented and incomplete insights. For example, one tool may track website visits, another monitors email engagement, and another handles paid ads—but none of them integrate seamlessly. As a result, marketers tend to overvalue the final interaction that triggered the conversion while undervaluing earlier touchpoints that influenced the buyer’s decision. This last-click bias can mislead teams into making inefficient budget and campaign decisions. To gain a true understanding of ROI, marketers need integrated analytics platforms and multi-touch attribution models that accurately account for all interactions along the buyer journey.
5. Privacy and Cookie Depreciation
Increasing privacy regulations and the gradual depreciation of third-party cookies are limiting marketers’ ability to track user behavior across websites and channels. This makes it harder to attribute conversions accurately and understand campaign performance.
As browsers phase out third-party cookies and regulations like GDPR and CCPA enforce stricter rules around data collection, marketers lose access to previously available tracking data. This affects the accuracy of measuring audience engagement, conversion paths, and multi-touch attribution. To adapt, B2B marketers need to rely on first-party data, invest in privacy-compliant tracking solutions, and implement robust consent management strategies. Without these adjustments, measuring marketing ROI becomes increasingly complex and potentially less reliable.
B2B Marketing Measurement Models and Methodologies
Unified Marketing Measurement Model
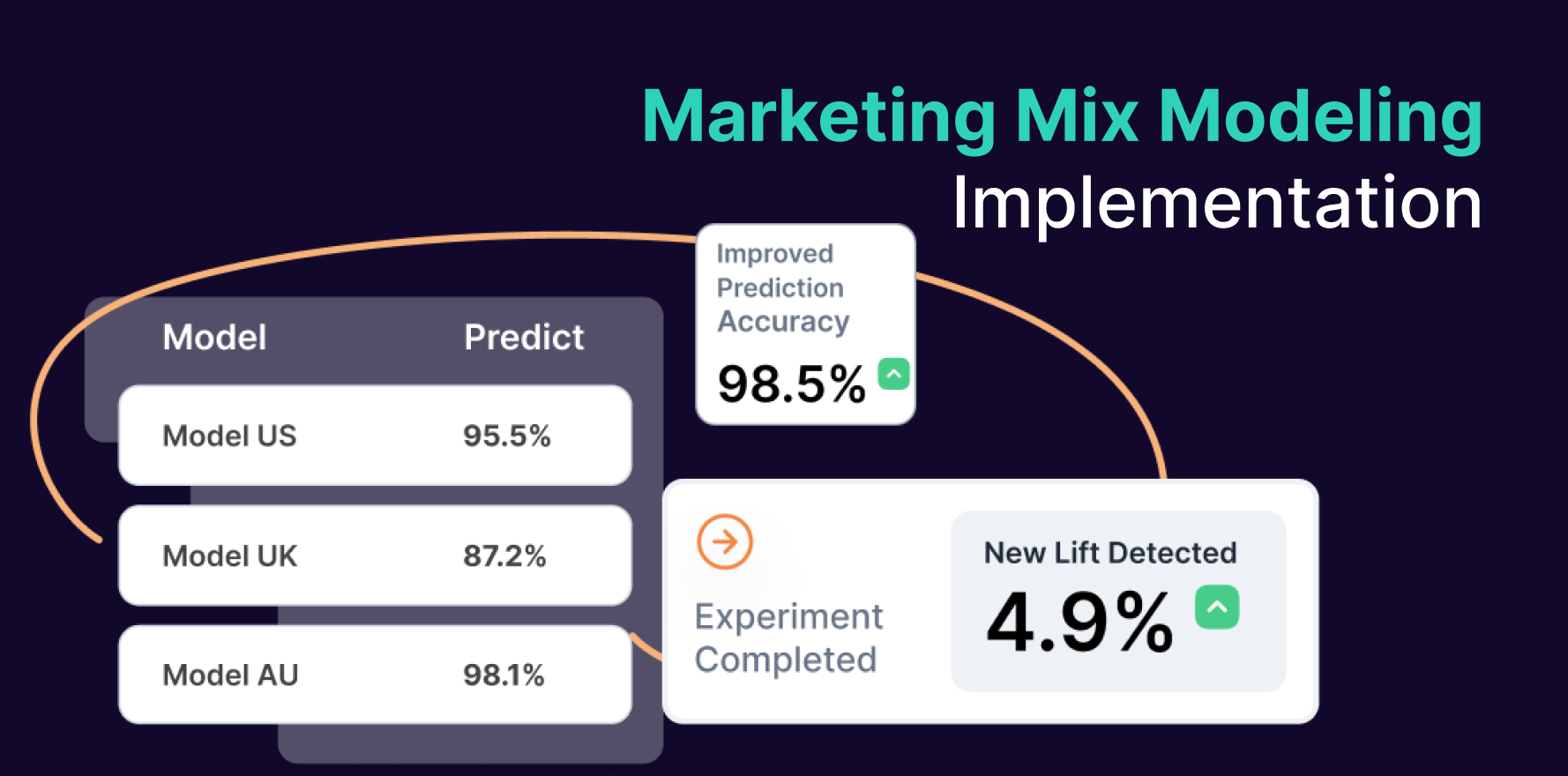
The Unified Marketing Measurement (UMM) model is an advanced framework that combines Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution. It provides a holistic view of marketing performance, enabling marketers to measure the effectiveness of campaigns across all channels, understand the true impact on revenue, and make data-driven decisions to optimize marketing spend.
UMM integrates multiple measurement approaches to overcome common challenges like fragmented tools, complex buyer journeys, and multi-touch attribution, giving B2B marketers a comprehensive, accurate, and actionable understanding of ROI.
1. Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM)
Marketing Mix Modeling is a statistical analysis technique that evaluates the impact of various marketing activities on overall business outcomes, such as sales, leads, or revenue. MMM uses historical data to understand how each channel, including TV, digital, email, social media, and events, contributes to performance.
MMM helps marketers identify which channels deliver the highest return on investment and how different tactics interact with each other. It is especially useful for long-term planning and budget allocation, allowing businesses to optimize spend across multiple campaigns and channels.
Key benefits include, Provides a high-level, aggregated view of marketing effectiveness, factoring in external influences such as seasonality, economic trends, or competitor activity.
2. Incrementality Testing
Incrementality testing measures the true incremental impact of a marketing activity by comparing the behavior of a treated group, which is exposed to the marketing campaign, against a control group, which is not exposed.
This method helps determine whether a campaign actually drove conversions or if results would have occurred naturally. It is particularly important in digital marketing, where overlapping campaigns or multiple touchpoints can make attribution misleading.
Key benefits include, Quantifies the actual lift from a campaign, allowing marketers to justify spend and optimize tactics that truly drive additional business value.
3. Causal Attribution
Causal attribution focuses on linking specific marketing actions to business outcomes, identifying which touchpoints or channels had a direct causal effect on conversions. Unlike standard attribution models, it looks beyond correlation to determine cause and effect relationships.
Causal attribution addresses the limitations of last-click or multi-touch attribution models, which can overemphasize certain interactions. By understanding which actions directly influenced buyer behavior, marketers can make more precise decisions about budget allocation and campaign optimization.
Key benefits include, Provides clarity on which marketing activities actually drive results, reducing guesswork and improving ROI measurement accuracy.
By combining MMM, Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution into a Unified Marketing Measurement framework, B2B marketers gain a comprehensive and accurate view of performance. This integrated approach overcomes challenges such as siloed tools, complex buyer journeys, and multi-touch attribution, enabling smarter, data-driven decisions to maximize marketing effectiveness.
How to Measure B2B Marketing Campaign Performance?
To start measuring B2B marketing campaign performance, begin by defining clear goals and KPIs, implementing privacy-first tracking, leveraging the UMM model, and continuously monitoring and optimizing performance based on the recommendations provided by the UMM model.
1. Define Clear Goals and KPIs
Before tracking any campaign, it’s essential to define what success looks like. Setting measurable goals ensures that marketing efforts focus on metrics that truly matter, such as leads generated, conversion rates, revenue influenced by marketing, engagement metrics like webinar attendance or content downloads, and customer acquisition cost (CAC). By establishing KPIs upfront, marketers can directly connect campaigns to business outcomes and align strategies with organizational objectives, ensuring that every action contributes to measurable success.
2. Implement Privacy-First Tracking
With the deprecation of third-party cookies and stricter privacy regulations, traditional tracking methods are no longer sufficient. Privacy-first approaches, including first-party data collection, server-side tracking, and consent management, allow marketers to maintain visibility into buyer behavior while staying compliant with GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations. These methods also help preserve accuracy in attribution and enable long-term tracking of complex buyer journeys, ensuring that marketing decisions are based on reliable and ethical data.
3. Leverage Unified Marketing Measurement
Unified Marketing Measurement (UMM) combines multiple measurement techniques, including Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution, to provide a comprehensive view of campaign effectiveness. This approach captures both short-term conversions and long-term brand impact, offering a holistic understanding of ROI. By integrating different methodologies, UMM allows marketers to evaluate performance across multiple channels, campaigns, and touchpoints, creating actionable insights for optimization and budget allocation.
4. Use Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM)
Marketing Mix Modeling evaluates the overall impact of various marketing channels on business outcomes using historical aggregated data. It answers questions like which channels drive the most revenue and where marketing budgets should be allocated. MMM provides macro-level insights, works even with limited individual-level tracking, and measures both short-term and long-term marketing impact, making it an essential tool for understanding how each channel contributes to overall business performance.
5. Conduct Incrementality Testing
Incrementality Testing isolates the true effect of marketing campaigns by comparing outcomes from a target group exposed to the campaign versus a control group. This method removes the noise of organic behavior and external factors, helping marketers identify campaigns that genuinely drive conversions. Incrementality Testing reduces reliance on biased attribution models and supports data-driven optimization, ensuring that resources are focused on initiatives that produce measurable results.
6. Apply Causal Attribution
Causal Attribution goes beyond correlation by determining which marketing activities directly cause desired outcomes. Using experiments and statistical models, it assigns accurate credit across complex buyer journeys. This approach works well with long B2B sales cycles and cookieless tracking environments, providing actionable insights for optimization and helping marketers focus on activities that truly influence ROI.
7. Continuously Monitor and Optimize
Measurement is not a one-time activity. Regularly reviewing campaign data allows marketers to adjust strategies, refine targeting, and reallocate budgets based on actual performance. Integrating all data sources into comprehensive dashboards ensures a single, accurate view of marketing effectiveness, enabling truly data-driven decision-making. Continuous monitoring and optimization help businesses stay agile, respond to market changes, and maximize the impact of every marketing dollar.
Key KPIs and Metrics to Measure for B2B Marketing Campaign Success
In modern B2B marketing, traditional KPIs alone are no longer sufficient. To truly understand the effectiveness of campaigns and optimize spend, marketers must track advanced, causal metrics that reflect real business impact.
Below are key KPIs and metrics that provide actionable insights when evaluated through a Unified Marketing Measurement (UMM) framework.
1. Return on Ad Spend: ROAS vs. Incremental ROAS (iROAS)
- ROAS measures total revenue generated from ads relative to total ad spend, but it doesn’t account for revenue that would have occurred naturally.
- Incremental ROAS (iROAS) isolates the true impact of ads by calculating the additional revenue caused directly by campaigns.
- iROAS is crucial for budget calibration within UMM, ensuring that every dollar spent contributes meaningfully to business outcomes.
2. Customer Acquisition Cost: CAC vs. Marginal ROAS (mROAS)
- While CAC provides a historical view of the cost to acquire a customer, marginal ROAS (mROAS) predicts the potential return on the next dollar spent.
- This forward-looking metric helps identify saturation points and informs decisions on scaling or adjusting campaigns, ensuring budgets are used efficiently.
3. Attribution vs. Incrementality
- Traditional attribution assigns credit along the buyer’s path, showing correlations but not causation.
- Incrementality measures the causal impact of marketing through experiments or statistical modeling.
- UMM combines both approaches, but prioritizes incrementality for validating campaign performance and making precise optimizations.
4. Forecasted Revenue vs. Measured Lift
- Forecasted revenue relies on predictive models based on historical performance, while measured lift comes from real-world experiments.
- Comparing the two allows marketers to refine MMM projections, preventing overconfidence in predictive models and ensuring campaigns are grounded in actual performance.
5. ROI vs. ROMI (Return on Marketing Investment)
- ROI measures overall business return, whereas ROMI isolates revenue driven solely by marketing activities.
- Within UMM, ROMI becomes more accurate when adjusted with incrementality insights from experiments and MMM, helping justify marketing investments and demonstrating the true value of campaigns.
6. CTR vs. Incremental Engagement Rate
- Click-through rate (CTR) tracks raw engagement, but it doesn’t reveal whether clicks were influenced by campaigns.
- Incremental engagement rate measures the additional engagement directly caused by ads, helping marketers focus on meaningful interactions that contribute to conversions.
7. Cost per Lead: CPL vs. Incremental CPL
- Traditional CPL divides total spend by leads generated, but incremental CPL identifies the cost of generating truly new leads attributable to a campaign.
- By isolating this metric, marketers can determine whether campaigns are creating additional demand or just capturing existing interest.
8. Brand Awareness vs. Brand Baseline Lift
- Brand awareness tracks visibility through surveys or media metrics, but baseline shifts reveal incremental changes over historical levels.
- UMM uses holdouts or test-control designs to measure baseline lift, helping marketers understand the long-term impact of campaigns on brand equity, not just short-term recall.
Best B2B Marketing Measurement Tools
1. Lifesight’s Unified Marketing Measurement Platform
Lifescight is an advanced Unified Marketing Measurement platform designed specifically for B2B marketers who need actionable insights across complex campaigns. It combines Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution into a single, integrated framework, allowing marketers to measure both short-term conversions and long-term brand impact.
Key features of Lifesight UMM include:
- Holistic ROI Analysis: Measure the true contribution of each marketing channel, accounting for multi-touch interactions and complex buyer journeys.
- Incrementality Insights: Determine which campaigns and actions are driving genuine lift in revenue and engagement, eliminating reliance on biased last-click attribution.
- Privacy-First Tracking: Compliant with GDPR, CCPA, and cookieless tracking, ensuring data accuracy while respecting user privacy.
- Actionable Recommendations: The platform provides practical insights and optimization suggestions, enabling marketers to adjust campaigns and budgets effectively in real-time.
- Integration Across Tools: Lifesight UMM unifies data from CRM systems, ad platforms, email campaigns, and content analytics into a single view for more accurate decision-making.
By leveraging Lifesight’s UMM platform, B2B marketers can move beyond traditional metrics, gain a true understanding of ROI, and make data-driven decisions that drive growth. It’s particularly valuable for organizations managing long sales cycles, multi-channel campaigns, and complex buyer journeys.
Read More: 6 Best Unified Marketing Measurement Platform
How to Get Started with Lifesight to Measure B2B Marketing Campaign and Efforts Effectively?
Getting started with Lifesight is simple and designed to help B2B marketers quickly understand and improve their marketing ROI (mROI).
STEP 1: Begin by visiting the Lifesight website to explore the platform’s features and capabilities.
STEP 2: Next, take a product tour to see firsthand how Unified Marketing Measurement, Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution work together to provide actionable insights.
STEP 3: Finally, book a personalized demo to discuss your marketing goals and see how Lifesight can be customized to measure your campaigns, optimize spend, and maximize ROI.
Following these steps ensures a smooth onboarding experience and sets your team up for more accurate, data-driven marketing decisions.
Conclusion
Effectively measuring B2B marketing performance is no longer optional; it is a business imperative. With challenges like complex buyer journeys, long sales cycles, and fragmented tools, traditional tracking methods are insufficient. By adopting advanced frameworks like Unified Marketing Measurement (UMM), leveraging techniques such as Marketing Mix Modeling, Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution, and using platforms like Lifesight, marketers can gain a holistic view of campaign effectiveness, optimize spend, and demonstrate clear ROI. Ultimately, accurate measurement empowers B2B organizations to eliminate guesswork, make data-driven decisions, and achieve sustained growth in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Essential resources for your success