Privacy concerns and tighter regulations have forced the advertising industry to pivot away from traditional cookie-based tracking methods, propelling contextual advertising into the spotlight. Unlike its predecessor, contextual advertising doesn’t rely on personal data collected over time but rather focuses on the content being viewed at a particular moment, aligning ads with the page’s theme or subject matter.
This approach promises a privacy-first strategy that doesn’t compromise on delivering relevant, engaging content to consumers. In this blog post, we’ll explore the resurgence of contextual advertising in a cookie-less world, discussing its benefits, implementation strategies, and its potential to reshape digital marketing.
What is Contextual Advertising?
Contextual advertising is a form of targeted advertising that involves displaying ads on a website or platform based on the web page’s content rather than the user’s previous browsing behavior. This method relies on the relevance of the webpage content to determine which ads to show, ensuring that the advertisements are directly related to the subjects the user is currently engaging with.
For example, a contextual ad system would display ads for running shoes and athletic apparel on a sports news article about marathon training.
Transitioning from the underlying principles of contextual advertising, let’s examine how it stands apart from its more invasive counterpart, behavioral advertising.
How does it differ from behavioral advertising?
In contrast, behavioral advertising collects data about a user’s browsing behavior over time, including the sites they visit, the links they click, and the searches they perform. This data is then used to create a detailed profile of the user’s interests, which advertisers use to serve targeted ads that are presumed to match the user’s preferences, regardless of the current webpage content they are viewing.
The key differences between contextual and behavioral advertising include:
| Aspect | Contextual Advertising | Behavioral Advertising |
| Data Used | It uses information about the webpage’s content where the ad is displayed. | Uses data collected about a user’s browsing history across multiple sites and sessions. |
| Privacy | It does not track user behavior across sites, focusing instead on the current page’s content. | Tracks user behavior across different websites to create targeted ad profiles. |
| Relevance | Ads are relevant to the content of the page currently being viewed. | Ads are based on the user’s past behavior and may not be relevant to the current page’s content. |
| User Experience | Enhances user experience by providing ads that are directly related to the content being engaged with. | It can disrupt user experience if ads are irrelevant to the current content. |
| Regulatory Compliance | It more easily complies with data privacy regulations because it does not involve extensive tracking of individuals. | Faces more challenges with privacy regulations due to its reliance on user tracking and data profiling. |
| Implementation | Simpler and generally less invasive, as it requires only an analysis of the current webpage’s content. | Requires sophisticated tracking technologies and data processing to analyze user behavior over time. |
Having looked into these key differences, let’s understand the concept behind contextual advertising.
How Does Contextual Advertising Work?
Contextual advertising begins by analyzing a webpage’s content when it loads, using technologies like Natural Language Processing (NLP) and semantic analysis. NLP identifies key phrases and topics, while semantic analysis delves into the meanings and relationships between words to ensure ads are highly relevant to the content.
After this analysis, the system matches and places ads that align with the content, such as fitness-related ads on a fitness webpage, enhancing user engagement due to their relevance. An ad server manages these ads to ensure they complement the content being viewed, making them more likely to capture user interest and drive interactions.
The effectiveness of these ads is continuously refined through feedback mechanisms like tracking click-through rates. Additionally, advanced systems dynamically adjust ads in response to content changes, maintaining ad relevance throughout the day. This sophisticated approach ensures that contextual advertising remains effective by aligning ads with the user’s current content engagement, enhancing user experience and ad performance.
Contextual advertising can also be categorized into several types based on how ads match content. Understanding these types can help advertisers choose the most effective campaign strategies.
Types of Contextual Advertising
Here’s a breakdown of the main types of contextual advertising:
1) Keyword matching:
This is the most basic form of contextual advertising. It involves matching ads to web pages based on specific keywords found within the content. For example, an ad for running shoes might appear on blog posts that mention keywords like “marathon training” or “running tips.”
This is best for simple and clear-cut content where key terms are well-defined and indicate the overall theme.
2) Topic targeting:
Ads are matched to web pages based on the content’s overall topic or subject matter. This method uses more sophisticated algorithms to understand the general theme of a webpage rather than focusing solely on specific keywords.
This is useful for broader campaigns where ads are relevant to general interests or subjects, such as sports, technology, or fashion.
3) Interest-based targeting:
While still respecting user privacy, interest-based targeting in a contextual framework involves displaying ads based on the inferred interests of the audience of a website or a specific web page, determined by the content they are consuming.
It effectively reaches broader audience segments whose specific interests align with their viewing content.
4) Semantic targeting:
Semantic targeting is a more advanced form of contextual advertising that analyzes the meaning behind the words used in content to ensure that ads are relevant to the deeper context, not just based on keyword occurrence.
This is ideal for complex topics with multiple meanings or nuances, ensuring ads are matched in the most relevant and sensitive manner.
5) Location-Based Contextual Advertising:
Ads are served based on the user’s geographic location as derived from the content or the context in which the user is engaged. This is particularly relevant for mobile users.
It is suitable for local businesses or events that want to target audiences in specific geographic areas.
6) Behavioral contextual advertising:
This type integrates some aspects of behavioral data but within the confines of a single session to maintain privacy. It observes user actions like clicks and time spent on specific content during a session to serve related ads in real time.
It enhances user experience by dynamically adjusting ad content based on immediate past actions without storing personal data.
Now, let’s explore the advantages of contextual advertising, which will help you understand why it’s becoming a favored strategy in digital marketing.
Benefits of Contextual Advertising
Contextual advertising offers significant benefits by ensuring ads match the content a user views, enhancing relevance without infringing on privacy. This alignment boosts user engagement by making ads feel like a natural part of the webpage and enhances the overall browsing experience.
Additionally, it simplifies the advertising process for marketers by eliminating complex tracking and data management, making it a cost-effective solution, particularly for businesses with limited budgets. This streamlined approach helps maintain user interest and increases the effectiveness of digital marketing campaigns.
In a LinkedIn post, Tanya Thorne, an accomplished CMO, shared her thoughts on why marketers should care about contextual advertising:
- Privacy Compliance: Navigate the digital space with respect for user privacy.
- Enhanced Engagement: Deliver ads that resonate with the content your audience loves.
- Future-Ready Marketing: Stay ahead in the game as we move beyond traditional behavioral targeting.
tanya-throne-linkedin-post-on-contextual-advertising 
Tips To Measure The Success of Contextual Advertising Campaigns
To effectively measure the success of your contextual advertising campaigns, it’s crucial to focus on several key metrics that reflect user engagement and conversion.
Tip 1: Monitor the click-through rates (CTR)
Monitor how often your ads are clicked relative to how often they’re displayed. A high CTR suggests that your ads are resonating well with your audience. Next, analyze the Conversion Rates to determine the percentage of clicks that achieve a desired action, such as a purchase or sign-up. This will reveal the direct effectiveness of your ads in driving specific outcomes.
Tip 2: Review the time on site for users who click on your ads.
Longer durations indicate that the content on your site is engaging and relevant. Conversely, check the Bounce Rates to identify how frequently visitors leave after viewing just one page. This could indicate mismatches between your ads and the landing page content or the content didn’t meet user expectations.
Tip 3: Calculating return on ad spend (ROAS)
Assess the profitability of your ads by comparing the revenue they generate against the cost of running them. This metric will help you gauge the financial efficacy of your campaigns.
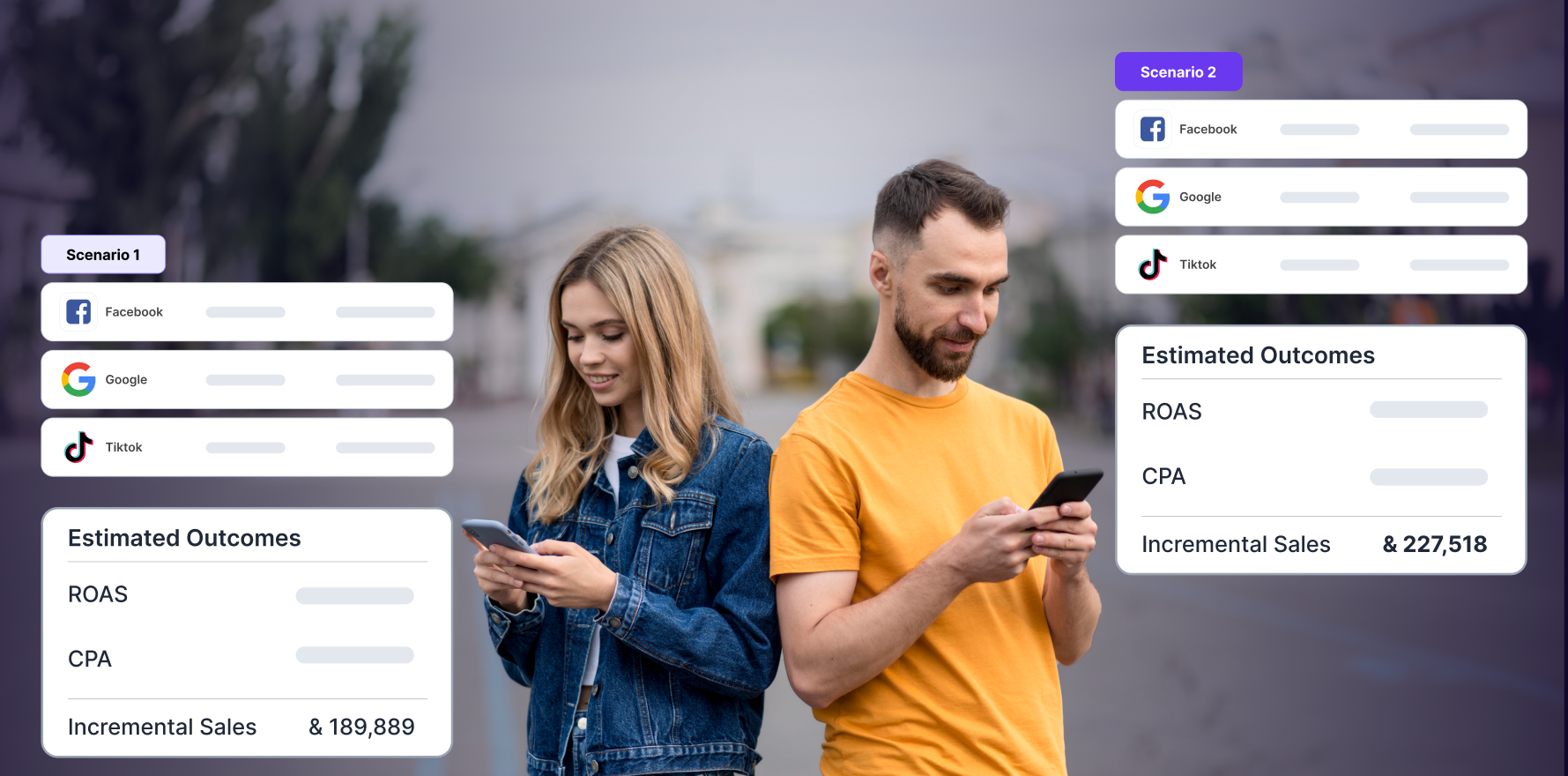
Tip 4: Use multi-touch attribution tools
Leverage any modern multi-touch attribution tool to optimize your marketing efforts. It provides a detailed framework that aids marketers in the decision-making process across various levels of advertising campaigns.
At the campaign level, decisions are shaped by strategic objectives established at the channel level.
At the granular level of individual ads or creatives, the focus sharpens further on direct performance metrics such as conversions, Return On Ad Spend (ROAS), Cost Per Acquisition (CPA), and the incremental lift each ad contributes.
Final Thoughts
As contextual advertising evolves, it’s set to harness AI advancements for improved precision and expand into new platforms like virtual reality. For marketers, staying informed about tech and regulatory changes, investing in semantic analysis tools, and constantly experimenting with ad placements will be key. Embrace these practices to ensure your strategies are both effective and future-proof.
FAQs on Contextual Advertising
1) What types of businesses can benefit from contextual advertising?
Almost any business can benefit from contextual advertising, especially those looking to target specific audiences with precise interests. This includes e-commerce stores, local service providers, tech companies, publishers, and other industries.
2) Is contextual advertising privacy-friendly?
Yes, contextual advertising is considered more privacy-friendly than other advertising types like behavioral targeting because it does not rely on personal data or user tracking. It only analyzes the context of the page, not the individual who is viewing it.
3) What strategies can enhance the effectiveness of contextual advertising?
To enhance the effectiveness of contextual advertising, consider the following strategies:
- High-quality content: Ensure the content is well-organized and rich in relevant keywords.
- Smart keyword selection: Choose keywords accurately reflecting the content and expected audience interest.
- Continuous testing: Regularly test different ads and strategies to optimize performance and ROI.
- Integration with other tactics: Combine contextual with other advertising strategies like retargeting to maximize impact.
You may also like
Essential resources for your success