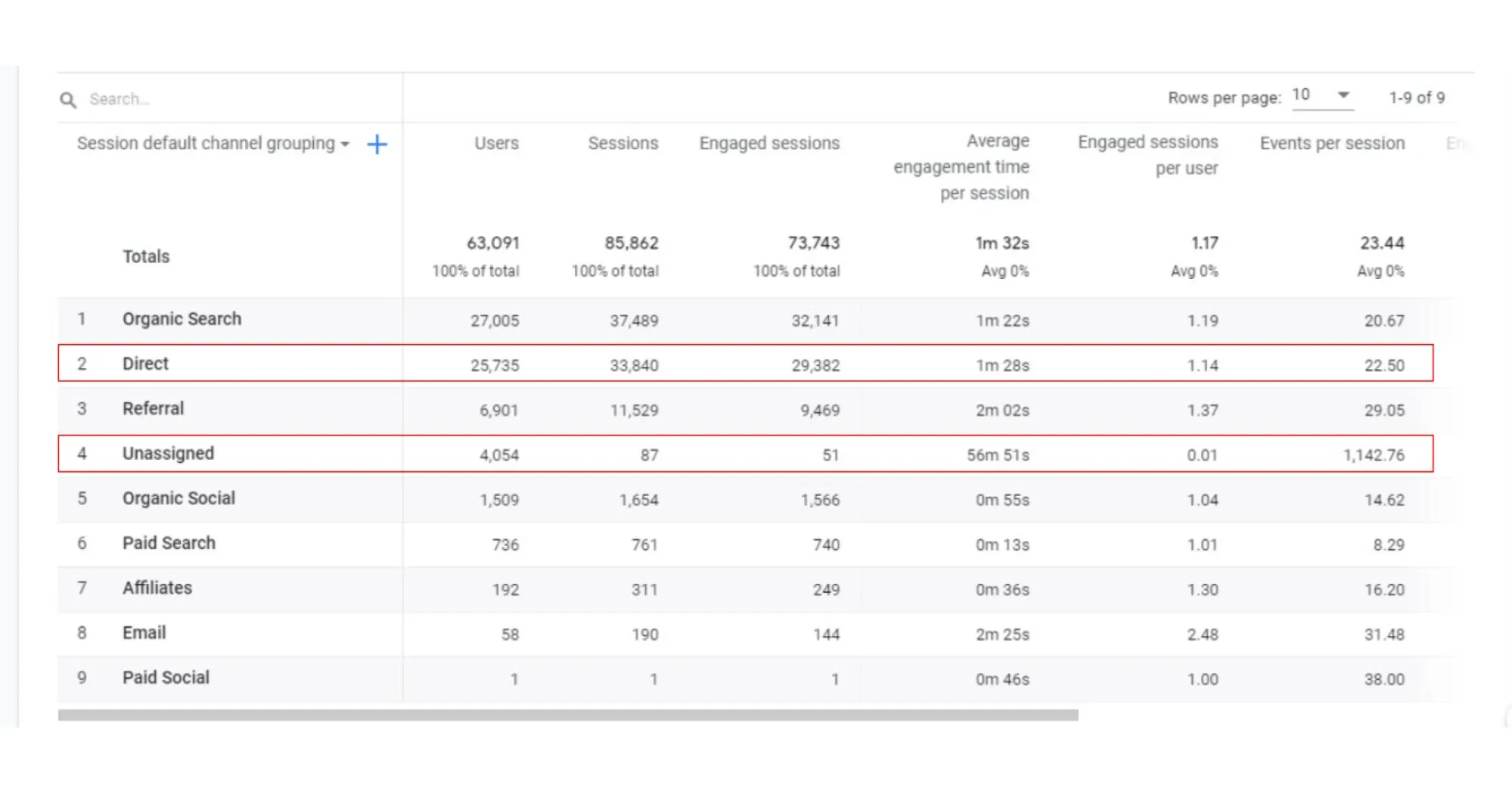
As a marketing analyst, have you ever looked at your business’s user acquisition snapshot on Google Analytics and wondered what exactly are the sources for the “direct” and “unassigned” traffic?
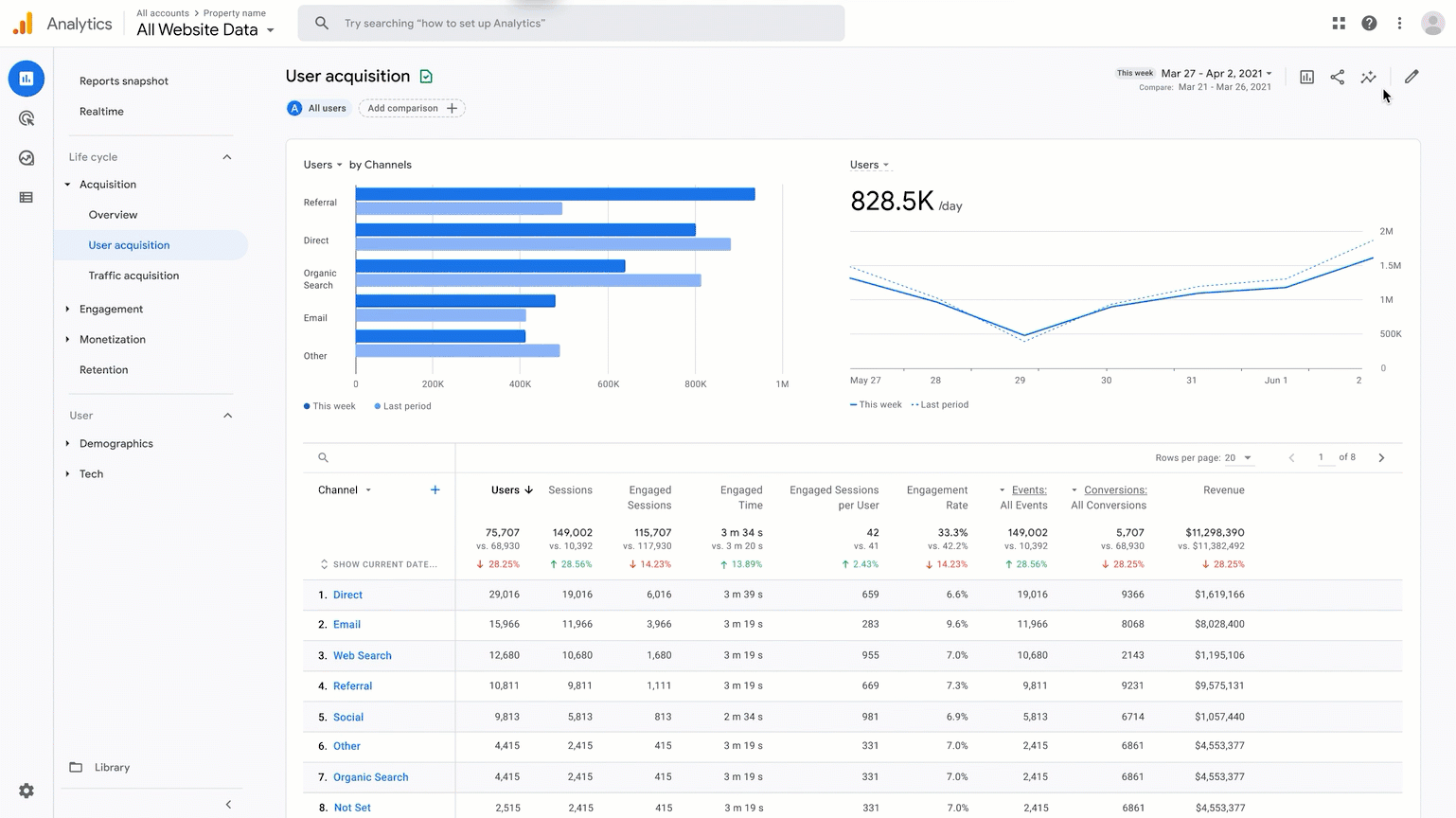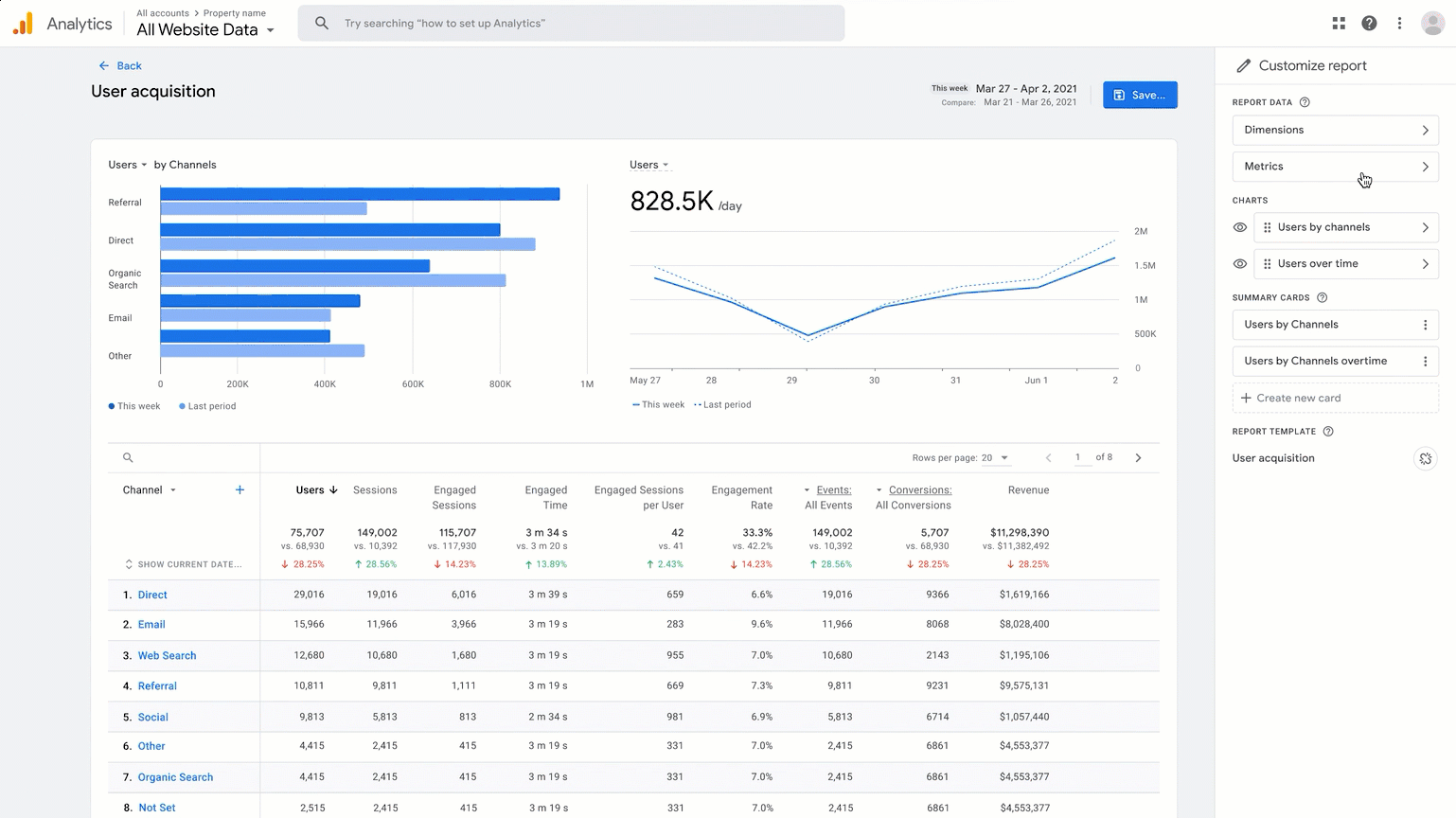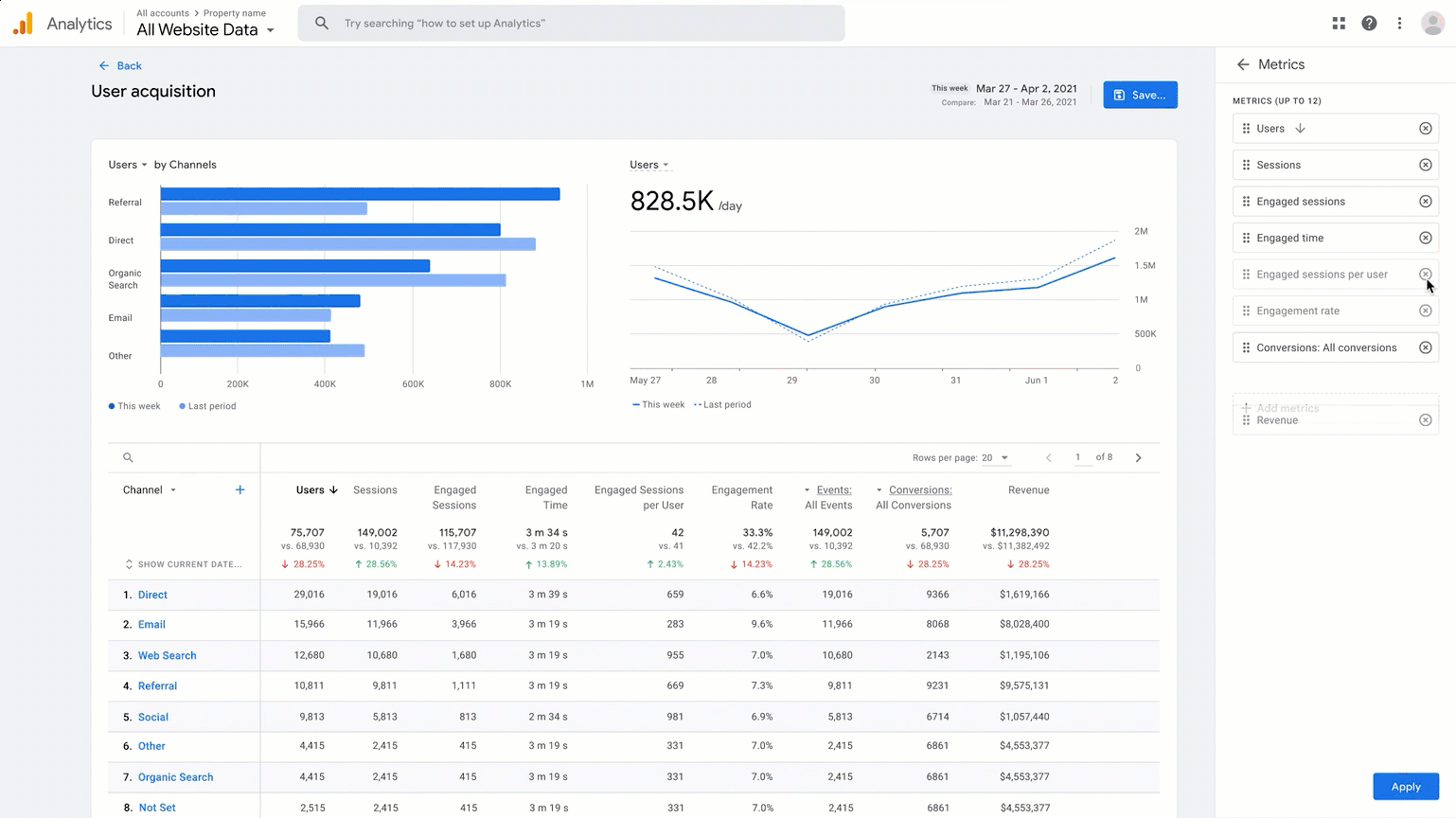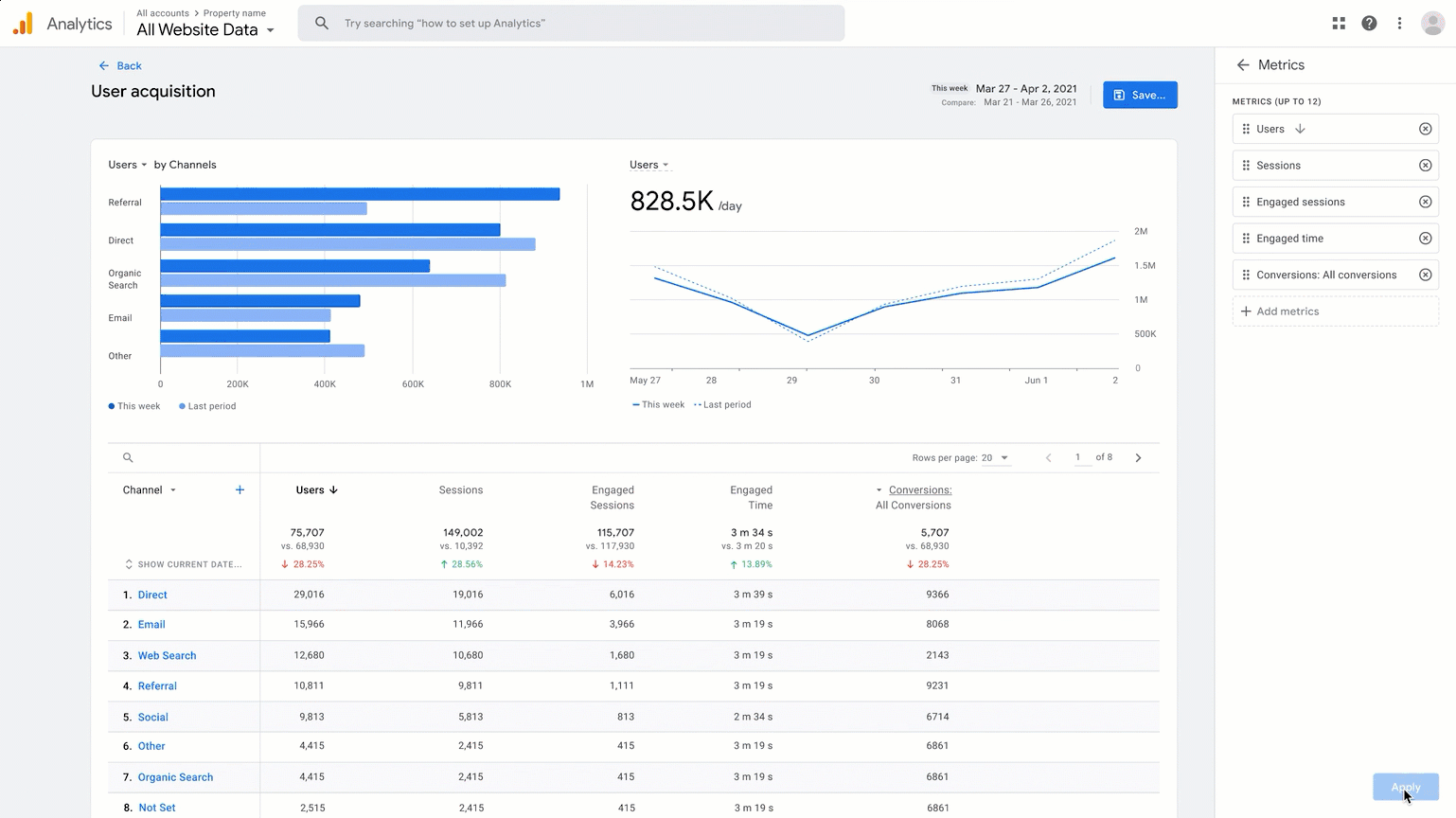
Google Analytics dashboard
A snapshot of the Google Analytics dashboard with “direct” and “unassigned” traffic sources highlighted. What exactly are they?
Google says that the traffic attributed as “Direct” refers to the website visitors who land on your website after typing in your URL directly into their browser or by bookmarking and revisiting your website later. On the other hand, “Unassigned” traffic refers to sessions that are not attributed to any particular traffic source or medium.
Our marketing analyst in particular went on a quest to get into the depths of these traffic sources and track them down to the tee. She used UTM parameters for every link possible to understand the true origin of these traffic sources. For an established business replacing thousands of links was a cumbersome task. But our analyst was hellbound to uncover the truth.
The result?
She still couldn’t identify the origin. Yes, the numbers for these traffic sources came down a little because of using UTMs, giving us an insight that even traffic from emails is sometimes counted under “Direct”. However, we still did not have clarity on what happens under the hood for these traffic sources.
So, we went on a new quest to gain a deeper understanding of Google Analytics.
How does Google Analytics work?
To keep things simple, we are going to look at Google Analytics in two distinct steps:
- The Data Gathering Process
- The Analysis Power
We will be providing the gist of both these steps without diving into the intricacies but we will make sure that you have enough information to go ahead and discuss it with your Marketing Data Scientist.
1) The Data Gathering Process
At its core, Google Analytics or GA is a tracking tool. It systematically collects data on website visitors and their interactions with the site. But the answer to its working lies in a clever interplay of JavaScript, cookies, and data science.
- JavaScript Magic: Google Analytics operates by embedding a small piece of JavaScript code into a website’s HTML. This code acts as a spy, gathering data on visitors” actions. It records everything from page views to button clicks, form subscriptions, and much more.
- The Cookie Trail: Cookies are the breadcrumbs in the digital realm. Google Analytics relies on cookies to identify and track users. When someone lands on a website, a unique client ID is assigned via cookies. This helps in recognizing returning visitors and aggregating data.
- Data Collection: When a user interacts with the website, the JavaScript code sends data to Google’s servers. This data is then processed and aggregated into comprehensive reports that include valuable information like the source of traffic, user demographics, the devices they use, and their behavior on the site.
2) The Analysis Power
Once the data is collected, Google Analytics offers a treasure trove of analytical tools. These tools provide businesses with the capability to dive deep into the data and extract actionable insights. It answers questions like: Who visits the site? How long do they stay? What are the most popular pages? What leads to conversions? The answers to these questions are usually presented in different reports.
gif showcasing Google Analytics 4’s reporting capabilities
A gif showcasing Google Analytics 4’s reporting capabilities. Source: Search Engine Journal
- Audience Analysis: Understanding your audience better with insights into their demographics, interests, and locations. This knowledge is invaluable for tailoring your content and marketing strategies.
- Acquisition Analysis: Analyzing the sources that drive visitors to your site. This can range from organic searches to social media referrals.
- Behavior Analysis: Delving into user behavior on your website. Learning which pages engage users the most and identifying potential bottlenecks in your conversion funnel.
- Conversion Tracking: Tracking your goals and measuring the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns. Google Analytics provides the data needed to optimize your efforts for higher conversions and ROI.
On the surface GA’s capabilities come across as a strong analytical tool. And do not get us wrong, it was, until the latest changes in the world of the internet and browsing.
The Limitations of Google Analytics: Navigating a Cookie-less World
In October 2020, Google launched the newest version of its analytics platform – Google Analytics 4. The main reason behind this significant change was the shift happening towards a cookie-less world and customers preferring a privacy-oriented browsing experience.
While Google Analytics 4(GA4) represents a significant leap forward in adapting to a changing digital landscape, it’s not without its limitations. In recent years, the world of online data collection has faced seismic shifts, and GA4 has had to adapt to new challenges in tracking user interactions effectively.
Let’s talk more about them….
Deprecation of Cookies
The deprecation of website cookies is perhaps one of the most formidable challenges facing GA4. Cookies, once the backbone of web tracking, are being phased out by browsers and privacy regulations. Users now have greater control over cookie tracking, and they’re becoming more cautious about sharing their data. This shift directly impacts GA4’s ability to monitor user behavior accurately.
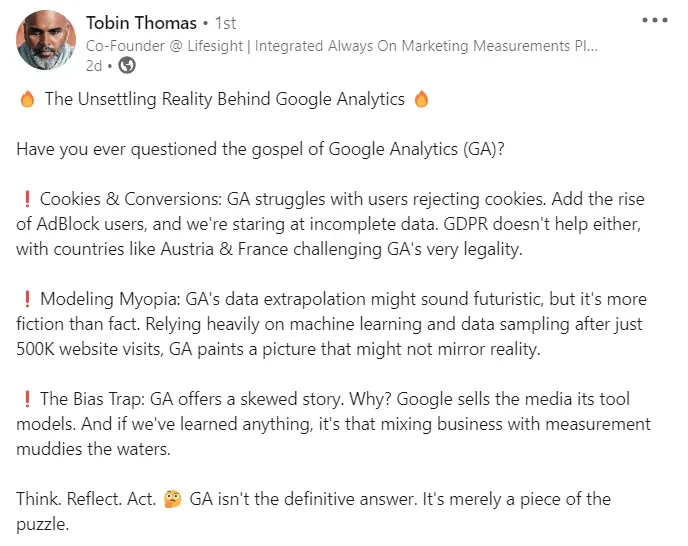
Deprecation of Cookies by Lifesight founder
Tobin Thomas, the founder of Lifesight, talking about how Google Analytics 4 falls short in accurate measurement and reporting. Source: LinkedIn
Without cookies, the reliability of tracking returning visitors and piecing together complete user journeys is compromised. Users’ ability to reset cookies or block them entirely further exacerbates this issue. The inevitable result is a fragmented view of user interactions on websites, making it difficult for businesses to get a comprehensive understanding of their audience.
Ad Blockers: Digital Shields Against Tracking
The rise in ad blocker usage is another obstacle for Google Analytics. Ad blockers are browser extensions or applications that prevent the loading of advertising content on websites. However, they have an unintended consequence – they block Google Analytics scripts as well.
This means that even if users have not explicitly opted out of web tracking through browser settings, ad blockers might be automatically doing so on their behalf. As a result, GA4 data is missing crucial insights from this segment of users, potentially underestimating website traffic and skewing user behavior data.
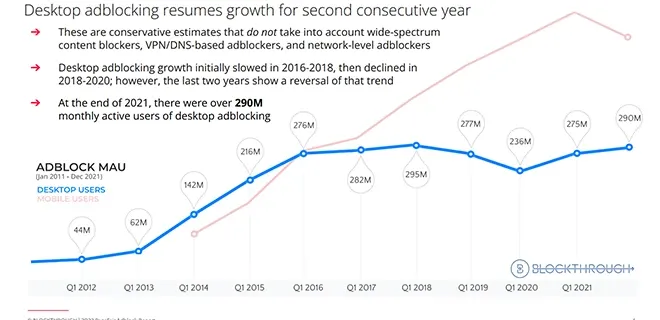
Ad blockers
Ad blockers have been growing over the past few years making tracking a hassle for marketers. The insurgence of privacy browsers too has added more weight to this challenge. Source: AdMonsters
The impact of ad blockers on tracking capabilities not only hinders the accuracy of visitor statistics but also raises ethical questions. Users employ ad blockers for privacy, security, and improved web performance. As such, businesses must navigate these challenges delicately, respecting user preferences while still seeking valuable insights.
So, what’s the road ahead?
Marketing Mix Modeling: A Path to Unbiased, Comprehensive Analytics
Where Google Analytics struggles with privacy and inaccurate tracking, Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) emerges as a robust solution, offering a path forward.
The Advantages of Marketing Mix Modeling:
- Privacy-Compliant Data Collection: One of the fundamental differences between MMM and GA is the way they handle data privacy. MMM respects user privacy by design, using aggregated data and modeling techniques, rather than relying on individual user tracking. This approach allows marketers to gather critical insights while adhering to evolving privacy regulations and user preferences, making it a more robust choice for privacy-compliant data collection.
- A Broader Perspective: Marketing Mix Modeling provides a more comprehensive view of your marketing impact. While GA4 excels at website and digital interaction tracking, MMM takes a holistic approach. It not only considers online channels but also offline media like TV, radio, and print advertising. This broader perspective is invaluable in understanding the real-world impact of marketing efforts.
- Statistical Rigor: Marketing Mix Modeling utilizes statistical techniques like regression analysis to understand the relationships between variables. This methodology provides more robust, quantifiable insights into marketing performance. It helps marketers move beyond surface-level metrics or intuition and dive deep into the data, uncovering what truly drives business results.
- Long-Term Forecasting: MMM isn’t just about the here and now. It enables marketers to forecast the long-term impact of their marketing activities. Businesses can plan and allocate resources more effectively by examining historical data and market conditions. In contrast, GA4 is often seen as a tool for immediate, short-term insights.
- MMM as a Privacy-Safe Solution: With an emphasis on maintaining privacy and complying with regulatory changes, Marketing Mix Modeling provides a reliable alternative in a post-cookie and privacy-legislated world. The legal hurdles posed by some privacy regulations are less of a concern when using MMM, giving peace of mind to marketers.
MMM in action: How Marketing Mix Modeling Works
To help you understand the possibilities MMM unlocks, we have taken the liberty of diving deeper into the mechanics of Marketing Mix Modeling with a practical example, utilizing Lifesight as our MMM tool.
As the first step, MMM needs data collected and sourced from all marketing channels possible. Instead of only relying on cookies, MMM needs data from various sources like your sales data, marketing expenses, customer data, competitor information, economic indicators, and data from ad platforms like Google, Facebook, and the like. The more variables you feed your MMM model, the more accurate will be the prediction.
Pro tip: Using a CDP can ease this task as it will have all your customer and business data in a single place.
Learn more about a CDP
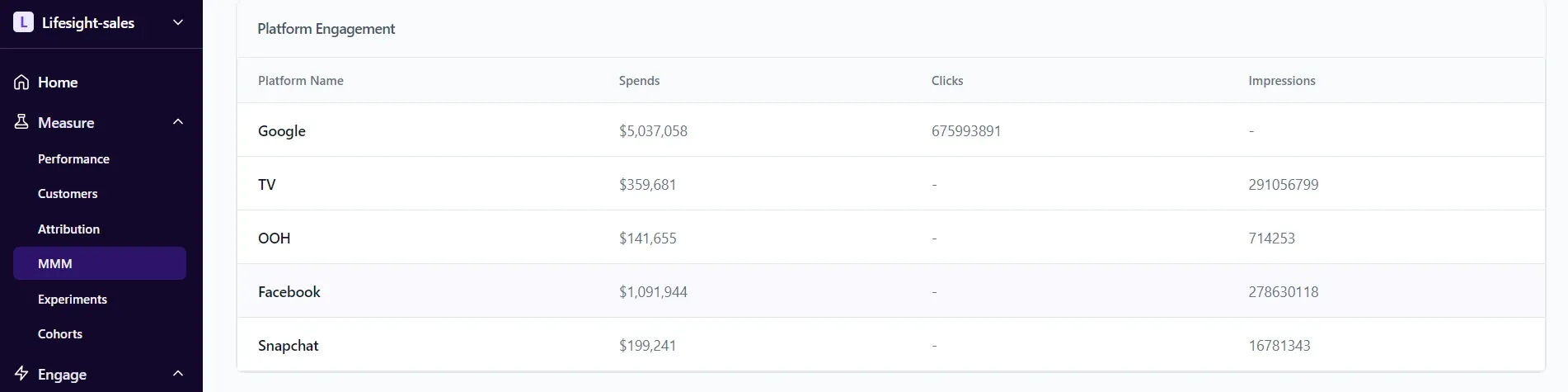
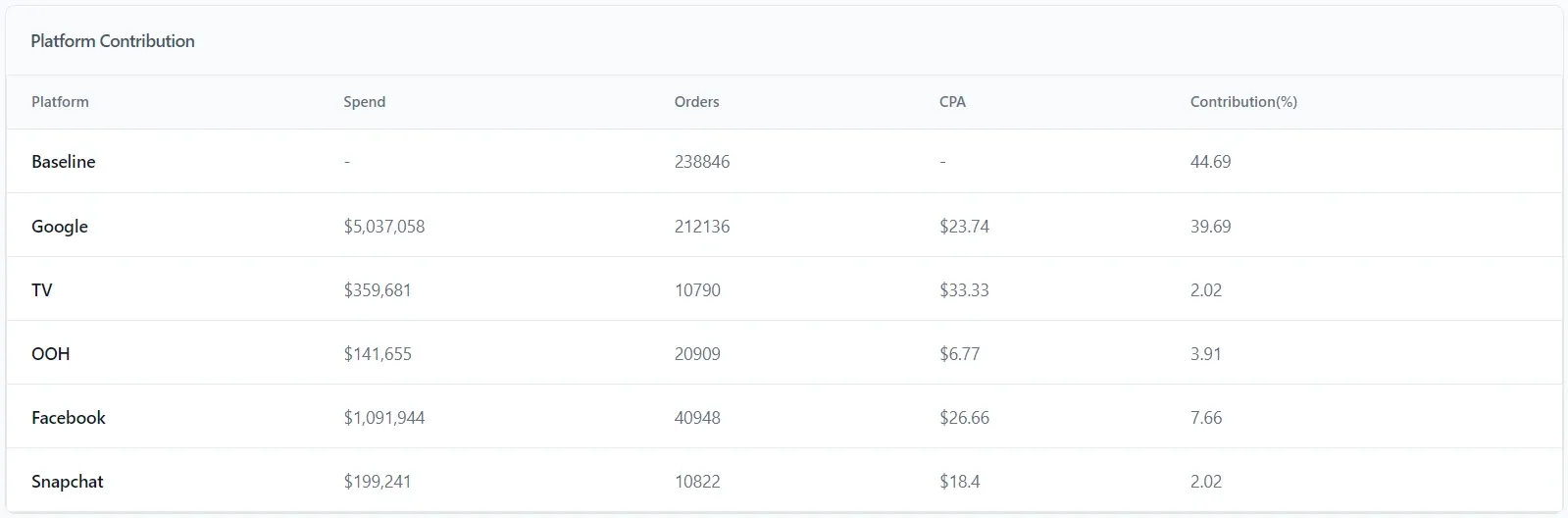
Since Lifesight comes with a CDP, we could easily pull the data for a food supplementary e-commerce brand that uses both online and offline advertising channels.
ecommerce brand’s primary spends pulled from Lifesight’s CDP
An ecommerce brand’s primary spends pulled from Lifesight’s CDP and seen on its MMM tab
Upon running this data through our MMM model, the brand got a comprehensive perspective that covers both online and offline channels, helping you understand how all marketing efforts contribute to the brand’s goals.
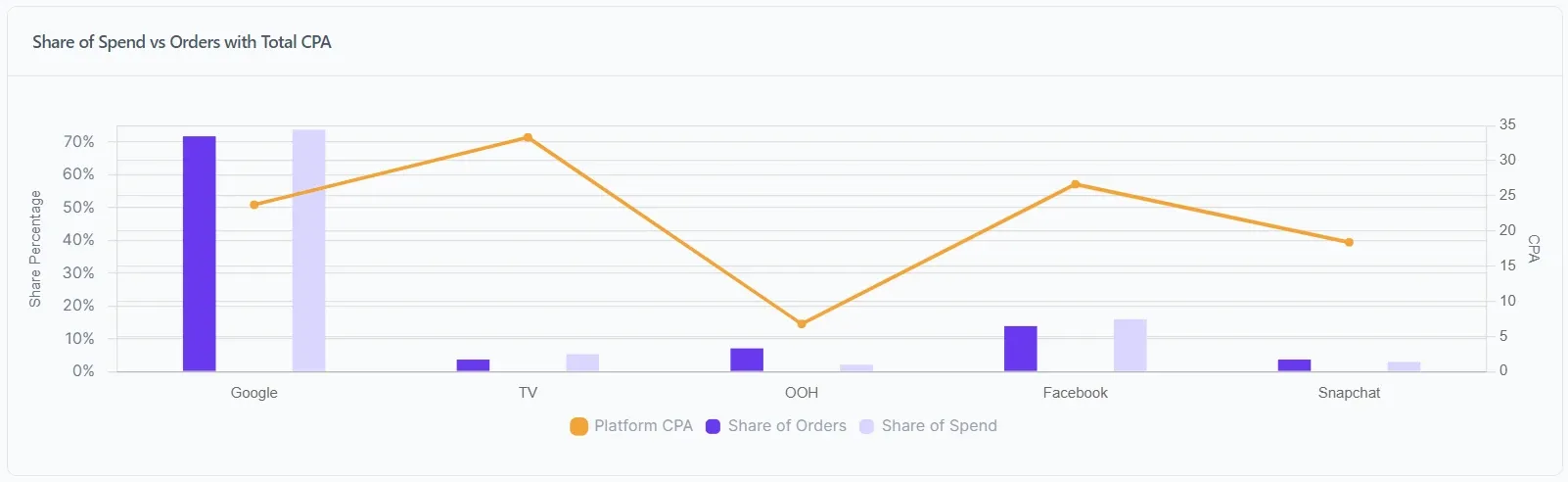
share of spend vs orders with total cpa
Lifesight’s MMM model showcasing how every advertising channel
Lifesight’s MMM model showcasing how every advertising channel, online and offline, have contributed to total revenue along with listing the platform CPA.
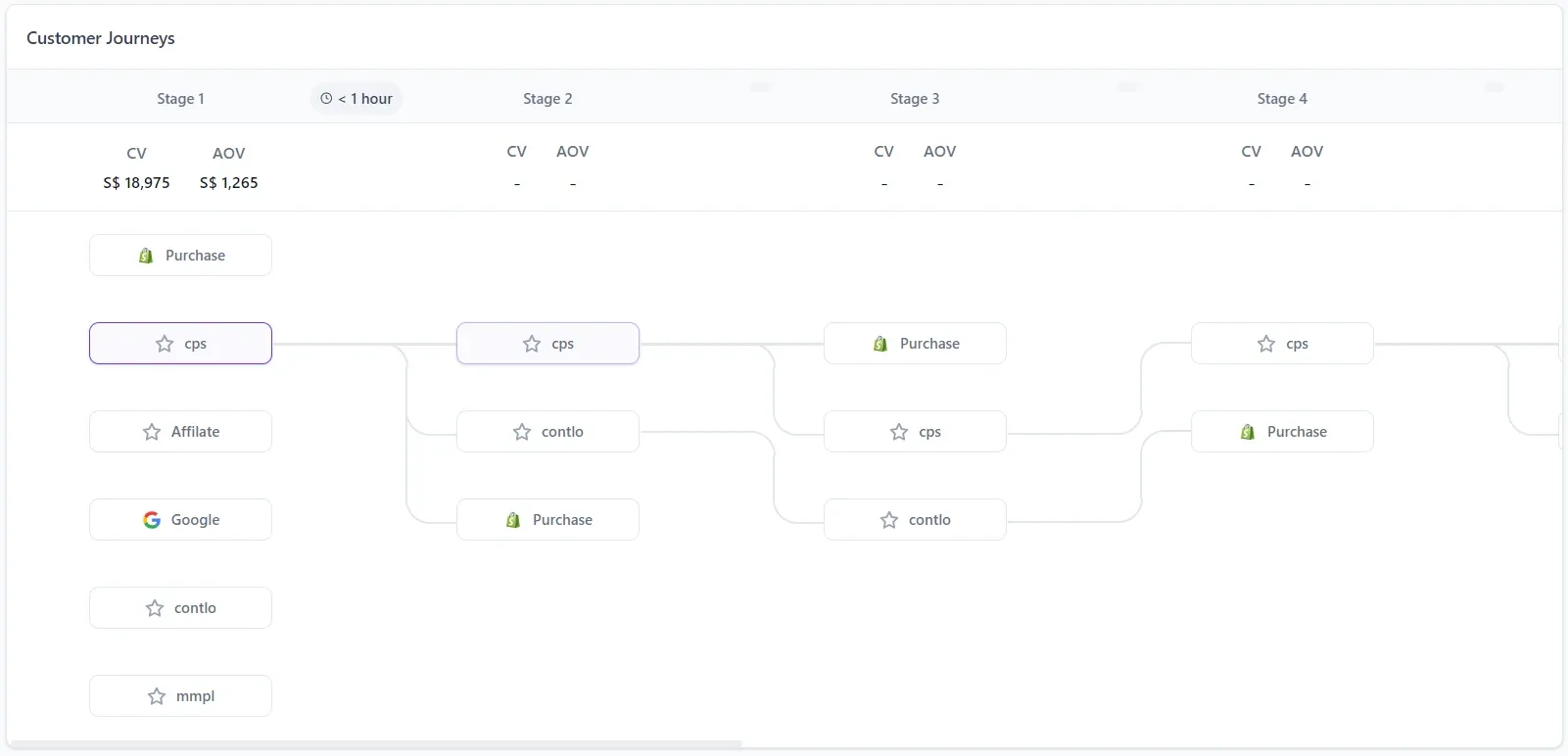
In order to help marketers understand the customers in a better way, Lifesight also provides the capability to dive deeper into the customer journeys and analyze how and when a sale happens.
Lifesight’s customer journey
Lifesight’s Customer Journeys feature in action showcasing how the platform not only helps you understand the revenue channels but also dive deeper into your customers’ shopping behavior
Conclusion: Evolving Beyond Google Analytics with Marketing Mix Modeling
The need for robust measurement and tracking tools has never been more critical. Google Analytics has been a steadfast companion for marketers, offering valuable insights into user behavior, website performance, and digital advertising effectiveness. However, as we’ve explored, it’s not without its limitations.
This is where Marketing Mix modeling emerges as a strategic alternative that marketers should consider. MMM offers a holistic and privacy-compliant approach to measuring the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
With its statistical credibility, MMM allows marketers to back their reports with hard data, enabling them to understand causation and correlations, not just surface-level associations.
Google Analytics remains a valuable tool for tracking digital interactions, but the changing digital landscape necessitates a more comprehensive approach to measurement. By considering MMM as part of their analytics toolkit, marketers can gain deeper insights and make more informed decisions.
If you’re interested in exploring the power of Marketing Mix Modeling, check Lifesight’s marketing mix modeling. Lifesight offers transparent, GDPR-compliant, and unbiased insights, helping you change the narrative, challenge the status quo, and drive genuine growth in your marketing strategies. Make data-driven decisions that move your business forward and discover the potential of MMMM today.
You may also like
Essential resources for your success