Marketing teams are battling shrinking budgets, rising ad costs, and vanishing data signals caused by privacy regulations and platform changes. With campaigns spread across dozens of online and offline channels, it’s harder than ever to pinpoint which strategies truly move the needle. The result is wasted spend, missed opportunities, and underperforming campaigns.
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) offers a way forward by transforming scattered data into clear, actionable insights that show what’s working, what’s not, and where every dollar delivers the most impact.
What is Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM)?
Marketing mix modeling (MMM) is one of the advanced marketing measurement models that helps businesses understand how different marketing efforts and strategies contribute to overall business outcomes such as sales and revenue.
To execute MMM, it is often built as a standalone tool or integrated into a unified marketing measurement (UMM) platform. MMM uses analytical methods such as multiple linear regression (MLR) and Bayesian statistics to analyze historical marketing data, including media spend, ad impressions, clicks, CPC, CPA, pricing, promotions, distribution, and external factors like seasonality or economic indicators.
This analysis incorporates both online and offline channels, helping to measure the true impact of various marketing activities on key business outcomes such as revenue, sales, and conversions.
To understand more about Marketing Mix Modeling, watch this video.
Example of Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM)
Imagine an e-commerce company that sells a wide range of products online and invests heavily in different marketing channels to drive traffic and sales. To optimize their marketing spend, they use MMM to analyze two years of historical data from both online and offline campaigns.
The historical data covers:
- Digital channels such as paid search (Google Ads), social media ads (Facebook, Instagram), email marketing, affiliate marketing, and display ads.
- Offline channels including TV commercials, print ads, and in-store promotions.
- Key performance indicators like ad impressions, clicks, CPC, CPM, CPA, pricing, promotions, and distribution coverage.
- External factors like seasonality (holiday sales, Black Friday), economic trends, and competitor actions.
Using multiple linear regression and bayesian statistics, MMM helps to measure each channel’s contribution to overall sales and customer acquisition.
For example:
The marketing mix model may reveal that paid search drives most conversions during regular periods, social media ads have a stronger impact during promotions, email marketing boosts repeat purchases, and affiliate marketing efficiently acquires new customers at a lower cost.
With these insights, the company can reallocate budget toward top-performing channels at the right times, optimize pricing and promotions, and reduce spending on underperforming tactics, resulting in improved return on ad spend (ROAS), higher customer lifetime value (CLV), and more efficient marketing investments overall.
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) Use Cases and Case Studies
1. Omni channel retail
A leading U.S. omni-channel retailer aimed to optimize both in-store and e-commerce conversions while driving full-price transactions and acquiring new customers without heavy discounting. By leveraging Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) within a unified measurement framework, they assessed the incremental impact of each marketing channel and campaign. This data-driven approach enabled them to refine their customer acquisition strategy and reallocate budget toward more profitable campaigns. The result was a 32% increase in incremental revenue, improved conversion rates, and reduced cost per acquisition.
Explore the full omni-channel retail case study to learn more.
2. Automobile
A Canadian automobile dealership struggled to pinpoint which marketing channels, both offline and digital, drove showroom visits and sales. By using Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), causal attribution, and geo experiments, they gained clear insights into channel performance, optimized budget allocation, and forecasted future results. This approach led to a 65% increase in incremental revenue, improved ROI, and sustainable growth through continuous testing and optimization.
Explore the full automobile case study to learn more.
3. Gaming
A $1 billion gaming company faced challenges measuring marketing impact after iOS privacy changes and signal loss. By implementing a custom Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) solution, they identified over-investment in saturated bottom-funnel channels and shifted spend toward top-funnel brand campaigns like CTV and offline media. This data-driven approach led to an 8% increase in incremental revenue, a 10% rise in game token purchases, and a 6% reduction in customer acquisition cost, all achieved without increasing budget..
Explore the full gaming industry case study to learn more.
4. FMCG
A leading FMCG retail company struggled to identify which marketing channels truly drove sales despite investing heavily across TV, radio, digital, print, and promotions. Using Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), they analyzed multi-year sales and marketing data along with external factors like seasonality and competitor actions. This helped uncover diminishing returns on TV, strong ROI from digital ads, and the value of seasonal promotions. By reallocating budget based on these insights, they achieved a 15% increase in marketing ROI and more confident, data-driven decisions, all without increasing overall spend.
Explore the full FMCG retail case study to learn more.
Benefits of Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM)
1. Provides a unified view of marketing performance
- Marketing Mix Modeling offers a unified analysis of overall marketing performance by combining data from both online and offline channels.
- It accounts for how different activities such as digital advertising, TV, radio, print, out-of-home (OOH), and in-store promotions interact and influence each other. It also considers external variables like pricing changes, competitor actions, economic shifts, and seasonality.
- This unified view helps marketers understand the true impact of each factor on business outcomes and ensures that all elements of the marketing strategy work cohesively toward a common goal.
2. Measures the impact of each marketing channel
- Marketing Mix Modeling uses advanced statistical and econometric models to isolate and measure the contribution of each marketing channel to business outcomes like sales, leads, or brand awareness.
- By controlling for various factors simultaneously, it helps distinguish which channels are truly driving performance.
- This data-driven insight allows marketing teams to make informed decisions about where to invest, optimize, or reduce spend for maximum effectiveness.
3. Captures both short-term and long-term marketing effects
- One of the Marketing Mix Modeling’s strengths is its ability to distinguish between short-term and long-term impacts.
- Short-term effects might result from promotions or flash campaigns that lead to immediate increases in sales.
Long-term effects come from consistent brand-building efforts such as TV advertising or sponsorships. - MMM models support both types of impact to help marketers strike the right balance between immediate results and sustained growth.
4. Privacy-compliant measurement without user-level data
- Marketing Mix Modeling uses aggregated and anonymized data instead of relying on individual-level tracking. This makes it naturally compliant with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- It is also resilient in a cookieless environment, making it a sustainable solution for measuring marketing effectiveness without compromising user privacy.
5. Enables smarter budget allocation
- With insights into which channels deliver the highest return on investment, Marketing Mix Modeling helps marketers allocate their budgets more strategically.
- It allows for the reallocation of funds from low-performing activities to those that deliver better outcomes.
- These insights support more confident budgeting decisions and contribute to stronger business performance.
6. Simulates scenarios for smarter forecasting
- Marketing Mix Modeling enables marketers to simulate and forecast the potential impact of different budget allocations and media mix scenarios based on historical performance.
- By analyzing past data, MMM allows for “what if” analysis, such as understanding what might happen if budgets are increased or shifted between channels.
- These forecasting capabilities help marketers plan more effectively, evaluate trade-offs, and make strategic decisions with greater confidence without the need for user-level data or real-time dashboards.
7. Drives higher ROI and marketing efficiency
- With a clearer understanding of what drives results through rigorous modeling, marketing teams can continuously refine their efforts for greater efficiency.
- Marketing Mix Modeling helps uncover underperforming tactics and highlights the ones that deliver strong results.
- Over time, this leads to better campaign performance and an overall improvement in marketing ROI.
8. Continuous improvement
- Marketing Mix Modeling is most effective when updated regularly. Recurring analysis helps businesses adapt to changing market conditions, shifts in consumer behavior, and new competitive threats.
- This ongoing process supports data-driven decision-making and fosters a culture of continuous optimization.
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) Components
The components of an MMM framework can be categorized into three main pillars:
1. Marketing inputs (Controllable variables)
These are levers that marketers can directly influence and are central to evaluating campaign effectiveness.
1.1 Media spend
Measures the impact of advertising across channels such as TV, digital, print, radio, and out-of-home.
1.2 Promotional activities
Includes discounts, coupons, seasonal promotions, and bundling strategies to drive short-term sales.
1.3 Product changes
Captures the effect of new features, packaging redesigns, or service enhancements on consumer response.
1.4 Pricing strategies
Evaluates how price fluctuations (increases or discounts) influence demand and revenue.
1.5 Distribution channels
Assesses the effectiveness of retail, e-commerce, DTC, and third-party distribution channels in reaching the customer.
2. External Factors (Uncontrollable Influences)
MMM models are built to explain and predict key performance metrics that matter to the business.
2.1 Sales
The total revenue or units sold, typically the primary outcome variable.
2.2 Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
The average cost to acquire a new customer, useful in ROI analyses.
2.3 Customer lifetime value (CLTV)
The predicted net profit from the entire future relationship with a customer.
2.4 Brand awareness
Often modeled as a secondary outcome, reflecting long-term brand-building effects.
3. Business Outcomes (Dependent Variables)
These are non-marketing elements that also affect business performance and must be controlled for in the model.
3.1 Seasonality
Includes holidays, weather cycles, and annual shopping events that naturally impact demand.
3.2 Economic conditions
Macro variables like inflation, GDP, and consumer sentiment that shift purchasing behavior.
3.3 Competitor activity
Accounts for shifts in market share driven by competitors’ marketing, pricing, or product changes.
3.4 Market trends
Long-term changes in consumer behavior, industry innovation, or societal preferences.
How Does Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) Work? A Step-by-Step Methodology
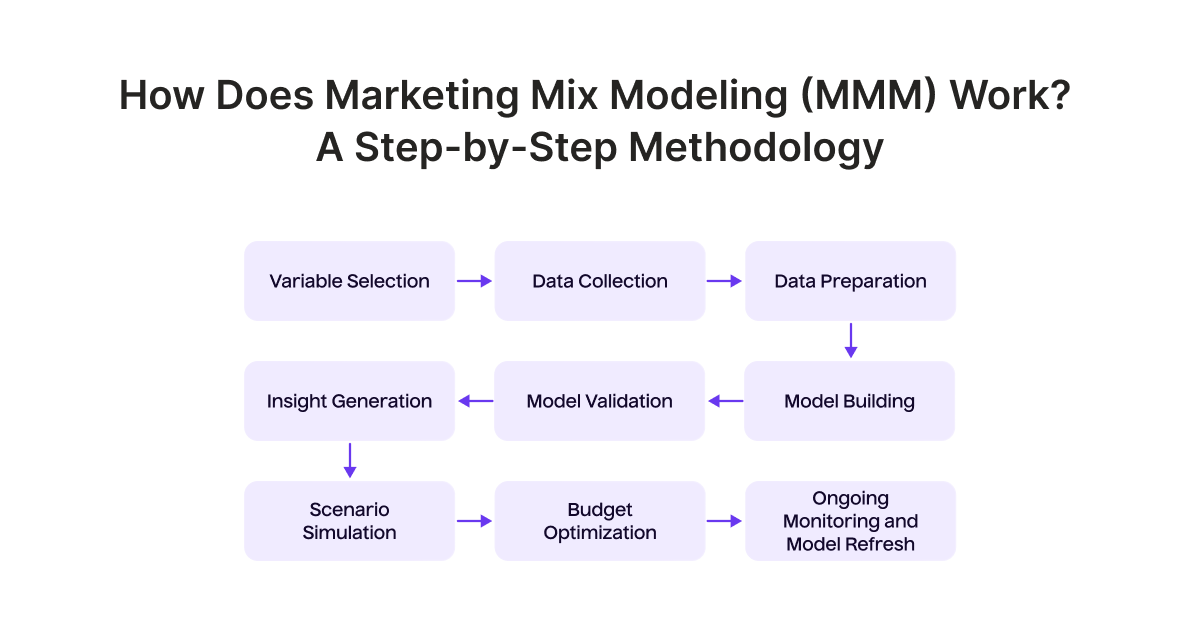
STEP 1. Variable selection
The process starts by identifying the key business outcome to be measured, such as sales, conversions, or revenue, and mapping all relevant independent variables that influence it. These include marketing inputs like media spend, impressions, CPC, CPM, CPA, along with pricing, promotions, distribution factors, and external variables such as seasonality, competitor activity, or economic trends.
STEP 2. Data collection
Once the variables are defined, historical data is collected from both online and offline sources, including ad platforms, CRM systems, sales data, promotional records, distribution data, and external datasets to build a comprehensive view of marketing activity and external influences.
STEP 3. Data preparation
The collected data is then cleaned and structured by aligning time periods, normalizing values, filling missing data, removing outliers, and formatting it into a time-series dataset ready for modeling.
STEP 4. Model building
Once the data is prepared, MMM statistical models such as multiple linear regression or Bayesian regression are applied to estimate the contribution of each variable to the business outcome while accounting for interaction effects and external factors.
STEP 5. Model validation
The model is validated for reliability by comparing predicted outcomes with actual historical results using techniques such as back-testing, cross-validation, or holdout datasets to ensure accuracy.
STEP 6. Insight generation
Once validated, the model provides detailed insights into the performance of marketing activities, highlighting ROI, ROAS, incremental impact, and identifying saturation points and diminishing returns for each channel.
STEP 7. Scenario simulation
Based on the generated insights, simulations are run to forecast future outcomes under different marketing mix scenarios, allowing data-driven planning and decision-making.
STEP 8. Budget optimization
Simulation outputs are then used to inform the optimal allocation of marketing budgets by shifting investment toward the most effective channels and strategies to maximize performance and return on investment.
STEP 9. Ongoing monitoring and model refresh
Finally, the model is continuously updated with new data and market changes to maintain accuracy and relevance, supporting ongoing measurement and optimization.
Advantages of Marketing Mix Modeling
1. Enhanced ROI analysis
MMM enables businesses to measure the return on investment (ROI) of various marketing activities, identifying which initiatives drive the most value and informing smarter investment decisions.
2. Optimized budget allocation
By quantifying the contribution of each marketing channel to business outcomes, MMM helps reallocate budgets towards the most effective channels, maximizing overall returns.
3. Data-driven decision making
MMM replaces guesswork with statistical insights, empowering marketers to make evidence-based decisions across campaigns and strategies.
4. Understanding channel performance
MMM identifies the most and least effective marketing channels and campaigns, enabling focused investment in high-impact areas.
5. Improved forecasting and sales prediction
By analyzing historical performance data, MMM helps predict future sales and the expected impact of marketing efforts, enabling proactive planning.
6. Identifying synergistic effects
MMM uncovers how marketing channels interact—revealing synergies where combined efforts perform better than individual ones.
7. Unified view of marketing performance
MMM offers a comprehensive unified marketing measurement view of all marketing activities, enabling a holistic assessment instead of siloed channel analysis.
8. Improved resource allocation
With clarity on the performance of each initiative, marketers can allocate resources, budget, personnel, and time more effectively.
9. Enhanced marketing strategy
Insights from MMM guide the refinement of overall marketing strategies, campaign designs, and tactical execution for long-term success.
Limitations of Marketing Mix Modeling
1. Data limitations
1.1 Data availability
MMM requires large volumes of high-quality historical data, which may not always be available or consistently tracked.
1.2 Data granularity
Lack of detailed data (e.g., daily or regional-level spend) can reduce model accuracy.
1.3 Attribution gaps
Offline and untracked touchpoints may lead to incomplete views of the customer journey.
1.4 Data lag
Delays in data availability can limit real-time or near-real-time decision-making.
2. Modeling limitations
2.1 Assumption-based
MMM relies on statistical assumptions that may oversimplify complex market dynamics.
2.2 Linearity bias
Traditional MMM often assumes linear relationships between spend and outcome, which may not reflect real-world diminishing returns.
2.3 Lag and decay estimation
Incorrectly estimated lag and decay effects can misrepresent the impact of marketing channels.
2.4 Limited causal inference
While MMM is good at correlation, it may struggle to prove causation without complementary methods (e.g., experiments).
3. Practical limitations
3.1 Time and cost intensive
Building and maintaining MMM models requires significant time, expertise, and financial resources.
3.2 Slow feedback loops
MMM typically operates on a monthly or quarterly cadence, limiting responsiveness to market changes.
3.3 Complex interpretation
Outputs can be difficult to interpret for non-technical stakeholders without proper visualization and explanation.
3.4 Requires continuous maintenance
Changes in market conditions, business strategy, or data sources necessitate ongoing model updates.
Best Marketing Mix Modeling Softwares and Tools
The best Marketing Mix Modeling software and tools include:
Read More About: Best Marketing Mix Modeling softwares for 2025
How to Create and Build a Marketing Mix Model with Lifesight? A Step-by-Step Guide
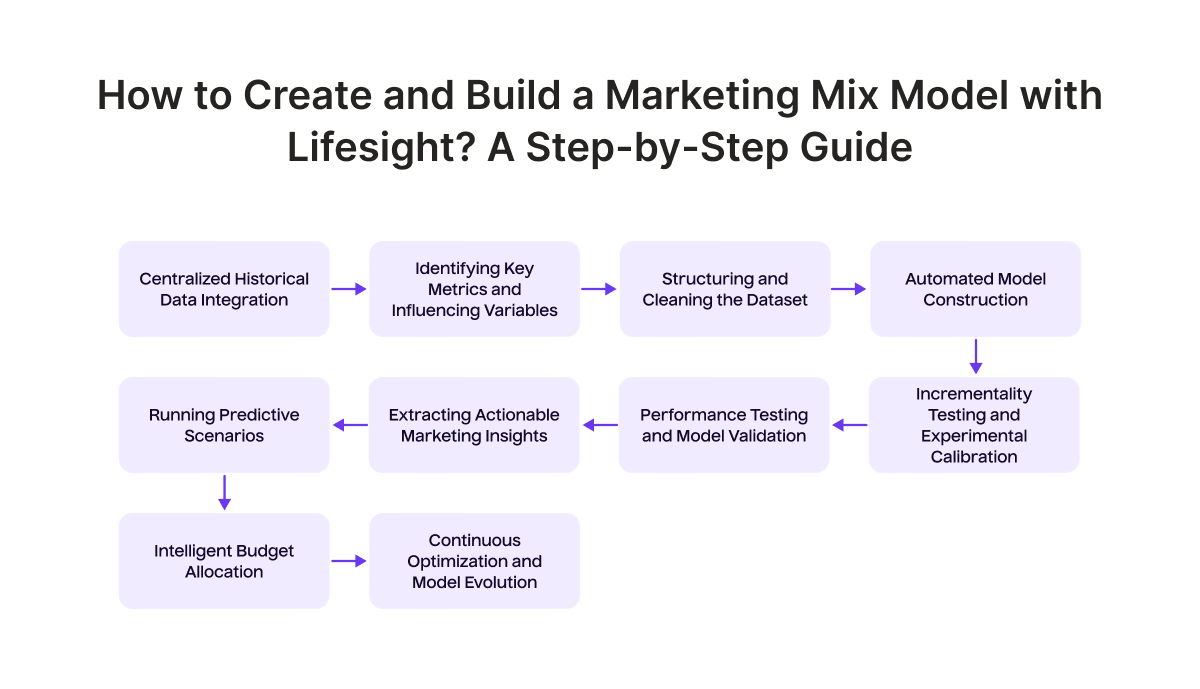
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create and build a Marketing Mix Model with Lifesight.
STEP 1: Centralized historical data integration
Lifesight integrates seamlessly with marketing and business tools, automatically gathering and unifying historical data from diverse sources including online ad platforms, CRM systems, offline sales logs, promotional records, distribution feeds, and external datasets such as seasonality and economic indicators.
This comprehensive aggregation ensures a complete view of marketing activities and the various factors influencing performance across all channels.
STEP 2: Identifying key metrics and influencing variables
With the data integrated, the next step is to define the primary business outcome to measure, such as revenue, conversions, or customer acquisition. Lifesight then automatically maps all relevant independent variables including media spend, impressions, CPC, CPM, CPA, pricing, promotions, distribution data, and external factors. Advanced variable transformation such as adstock and saturation effects are also applied.
STEP 3: Structuring and cleaning the dataset
The platform cleans the collected data by aligning time periods, normalizing metrics, filling in missing values, and removing outliers. Data is then formatted into a consistent time-series dataset optimized for modeling.
STEP 4: Automated model construction
Lifesight applies statistical and machine learning models, such as multiple linear regression and bayesian statistics, to estimate the contribution of each variable to the defined business outcome. The model accounts for interaction effects, lagged responses, and nonlinear relationships between variables.
STEP 5: Incrementality testing and experimental calibration
To enhance model accuracy, Lifesight integrates incrementality testing methods such as geo-experiments and A/B lift tests. These controlled experiments measure the true incremental impact of marketing activities, providing real-world lift data that calibrates and validates modeled channel contributions.
STEP 6: Performance testing and model validation
The model undergoes rigorous validation using holdout datasets, back-testing, and cross-validation techniques to ensure robustness and predictive accuracy.
STEP 7: Extracting actionable marketing insights
Validated models generate detailed insights highlighting ROI, ROAS, incremental impact, and diminishing returns across marketing channels. These insights enable data-driven decisions on channel performance and saturation points.
STEP 8: Running predictive scenarios
Lifesight enables scenario planning by simulating how adjustments in media spend, channel mix, or external conditions might affect future business outcomes. This supports informed forecasting and strategic planning.
STEP 9: Intelligent budget allocation
Simulation outputs feed into an optimization engine that recommends budget shifts toward the most effective channels and strategies. This maximizes ROI by prioritizing investments informed by both modeled results and incrementality testing.
STEP 10: Continuous optimization and model evolution
The model is refreshed regularly with new data and market updates to maintain accuracy and relevance. Ongoing monitoring ensures marketing strategies remain aligned with evolving consumer behavior and external factors.
How to Evaluate Marketing Mix Modeling Platforms?
To evaluate Marketing Mix Modeling platforms, focus on how well each platform addresses the challenges of marketing measurement.
Criteria for Evaluating MMM platforms
- Data Integration & Aggregation
- Analytical Methods & Modelling Techniques
- Measure all channels Online & Offline
- Privacy & Complaince
- Incrementality Testing & Validation
- Actionable Insights & Forecasting Scenario
- Continuous Model Refresh & Usability
- Optimization & Recommendations.
Lifesight is recommended because it evaluates all key criteria of Marketing Mix Modeling, enabling marketers to make data-driven decisions and maximize marketing ROI confidently.
How Lifesight Helps Get Started with Marketing Mix Modeling?
Getting started with Marketing Mix Modeling is simple with Lifesight. Just book a demo, and one of our experts will walk you through the platform and show you how easy it is to connect your data, build models, and get actionable insights.
The platform automates everything from data integration to modeling and recommendations, helping you quickly measure, plan, and forecast marketing impact across all channels. This ultimately helps you improve your ROAS.
Streamlined data → Actionable insights → Maximum ROAS
Conclusion
Marketing Mix Modeling is no longer just a tool for large enterprises. It is an essential capability for any brand looking to grow efficiently in today’s dynamic marketing environment. By moving beyond siloed metrics and embracing data-driven decision-making, marketers can finally understand the true impact of their efforts.
Lifesight’s Causal Marketing Mix Modeling platform makes this transformation simple. From seamless data integration to actionable insights, Lifesight provides everything you need to measure, optimize, and scale your marketing strategies with confidence.
Smarter marketing starts with better measurement. Book a demo today and take the first step toward more effective, ROI-driven marketing.
FAQ
1. What does mmm stand for in marketing?
MMM stands for Marketing Mix Modeling. It is a statistical analysis technique used to estimate the impact of various marketing activities on business outcomes like sales or revenue.
2. What is mixed media modelling?
Mixed media modeling refers to analyzing how different media channels (e.g., TV, digital, print, radio) contribute to business results. It is often used interchangeably with Marketing Mix Modeling, though MMM is more comprehensive in incorporating pricing, promotions, and external factors.
3. What is the role of Marketing Mix Modeling?
The role of MMM is to quantify the effectiveness of marketing activities, helping businesses understand what’s driving performance. It supports better decision-making by identifying high-ROI channels and guiding budget allocation.
4. What business problems can MMM solve?
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) helps businesses solve key problems like identifying which marketing channels are most effective, optimizing budget allocation, and measuring the overall impact of marketing activities. By providing data-driven insights, MMM enables companies to make smarter decisions and improve their return on investment (ROI).
5. What do marketing mix models show advertisers?
Marketing mix models show advertisers:
- The contribution of each marketing channel to sales or other KPIs
- The ROI of individual marketing tactics
- Synergies between channels
- Forecasts for future performance under different budget scenarios
6. What are the 4Ps of the marketing mix model?
The 4Ps are the foundational elements of the traditional marketing mix:
- Product – What you’re selling
- Price – The pricing strategy
- Place – Where the product is distributed to customers?
- Promotion – How the product is marketed?
7. What are the 7 C’s of marketing mix?
The 7 C’s offer a customer-centric alternative to the traditional 4Ps:
- Customer – Focus on needs and wants
- Cost – Total cost to the customer (not just price)
- Convenience – Ease of purchase
- Communication – Two-way interaction with customers
- Credibility – Trust in the brand
- Customer Service – Post-purchase support
- Consistency – Uniform brand experience across touchpoints
8. What are the 7Ps of the marketing mix model?
The 7Ps expand on the original 4Ps to include services and customer experience:
- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotion
- People – Employees and customer interaction
- Process – Delivery and service mechanisms
- Physical Evidence – Tangible cues like packaging or branding
9. How to use marketing mix modeling?
To use MMM:
- Gather historical data on sales and marketing activities
- Build a statistical model (e.g., regression) to estimate impact
- Analyze results to identify high-performing channels and drivers
- Apply insights to optimize marketing budgets and forecast outcomes
- Continuously update the model as market conditions and campaigns evolve
10. What is the difference between MMM and marketing attribution?
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) evaluates how total marketing investments across channels and external influences drive overall business results, whereas marketing attribution identifies and credits the specific customer interactions that lead directly to a conversion.
11. How do privacy changes (like iOS updates) affect MMM?
Privacy changes in iOS, including updates in iOS 14 and 17, have made tracking user-level data more difficult, complicating Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) efforts to measure campaign effectiveness and allocate budgets accurately. To address this, Causal Attribution leverages advanced statistical techniques and controlled experiments to identify the true impact of marketing activities despite data restrictions.
12. How long does it take to implement an MMM solution?
Creating a custom Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) solution can take several months due to the complexities involved in data collection, cleaning, and model development. In contrast, purchasing ready-made software solutions such as Lifesight, Funnel, or Rockerbox provides a faster and easier alternative, enabling quicker implementation and actionable insights without the need to build a model from scratch.
13. How often should MMM be updated?
Traditional Marketing Mix Models are typically refreshed quarterly or biannually to account for shifts in market conditions and consumer behavior. In contrast, advanced MMM software solutions enable more frequent updates, often on a monthly basis, allowing for faster adaptation to changing marketing dynamics and more timely insights.
You may also like
Essential resources for your success