Walking by the brick-and-mortar stores has become common to us, while we see a few customers stepping in to make one or the other purchases, it isn’t a denial that online ecommerce stores gain traction as well.
To bring it to your notice, the ease and convenience that an online shopping platform gives can’t be felt in the physical stores. It would put you into thinking if you know that 50.8% of consumers say free shipping is one of the top motivating factors as to why customers choose online over offline as it would save them from having to spend a little extra money in traveling to shop from a physical store.
But adding the clause that they also receive quick delivery, let’s say in a day as agreed by 27.7% of users. As it also gives an easy return policy that can’t be expected in a physical store once purchased. The 38.7% shoppers say the offers and discounts received on the products are like nowhere else.
If you’re thinking about or on the path to building an ecommerce business, we cover the 6 different types of ecommerce business models and how to choose the best one for your brand.
What is an ecommerce business model?
Ecommerce represents an online business model that allows businesses to sell products and consumers to buy products in a virtual mode without physical intervention while experiencing the look and feel of the product with a scroll of your phone. Technically giving consumers the leverage to shop at their convenience.
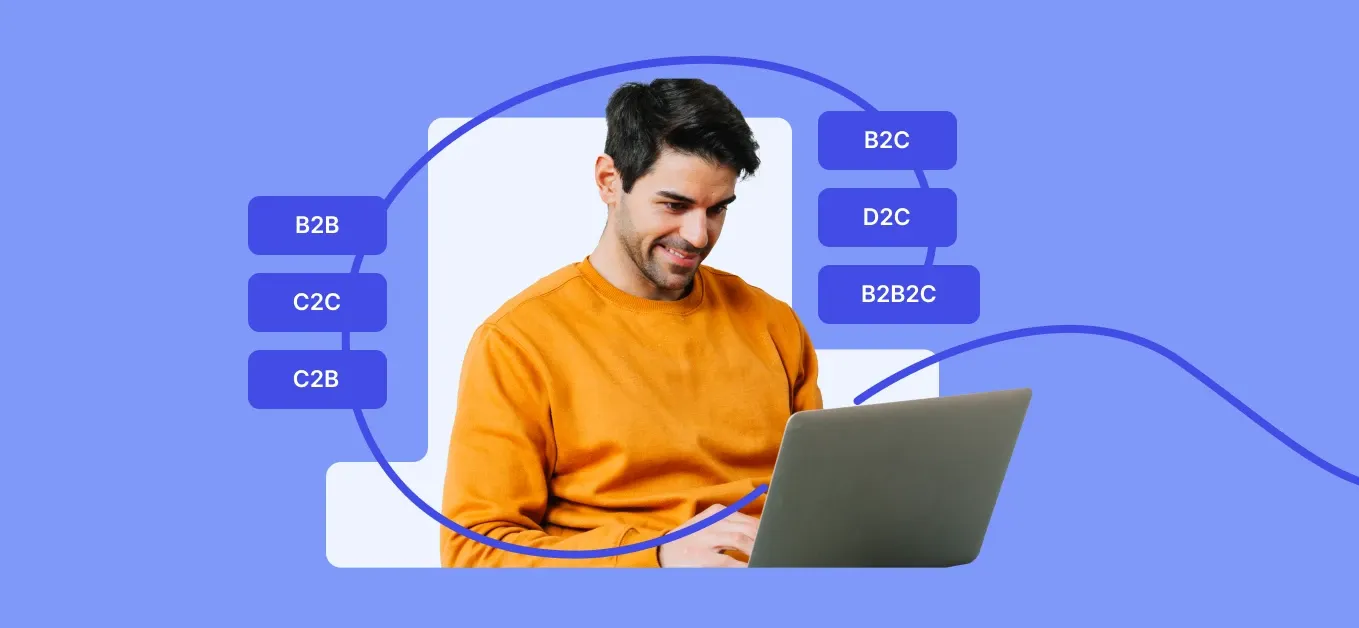
Different types of ecommerce business models
B2B
B2B stands for Business to Business ecommerce. A B2B business model harnesses modern digital commerce processes and facilitates transactions between two businesses.
ecommerce business models-B2B-Alibaba 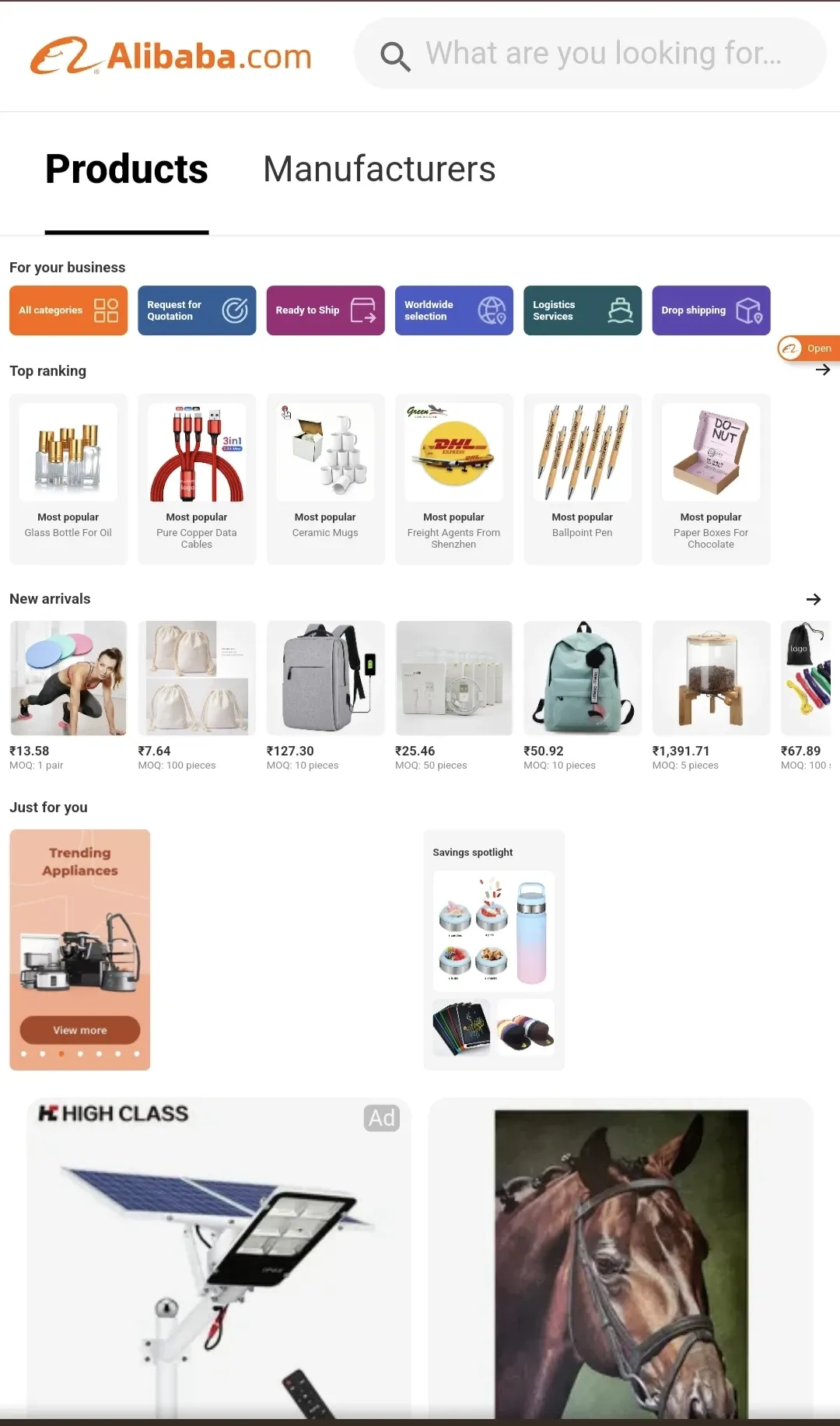
Alibaba, is the largest B2B ecommerce company to look at, with nearly 20 million sellers and buyers from 240 countries.
Whether you are a manufacturer or a wholesale supplier, B2B business models can be the right fit to market to the buyers or vendors.
B2C
The B2C ecommerce business model is about selling it directly to the consumers and doesn’t have intermediaries. It makes space for businesses ranging from small operations to giant conglomerates to sell directly to customers.
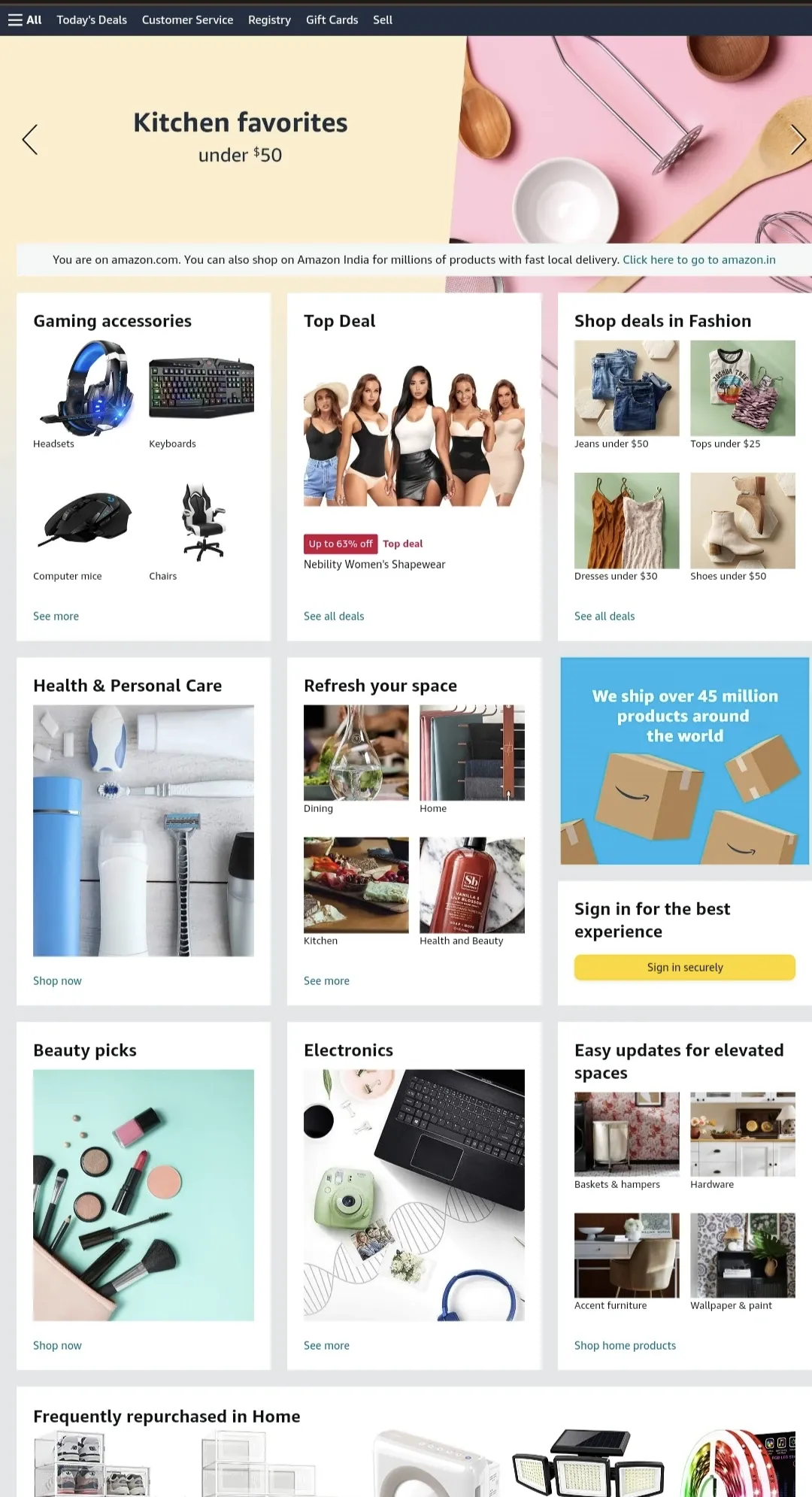
ecommerce business models-B2C-Amazon
One such example would be Amazon’s ecommerce business model. It is a marketplace with a vast product range catering directly to consumers. They ensure to provide a seamless experience to the customer throughout their journey.
Business-to-consumer ecommerce model is beneficial to businesses that sell to the customers directly aiding in shortening the sales cycle. Many sellers on Amazon also operate under a B2C model when they retail products sourced in bulk.
Also adding to the purchase that is driven emotionally. Sectors that seek to build a direct relationship with the customers and want to impact the purchases with an emotional marketing message see this business model as a fit.
C2C
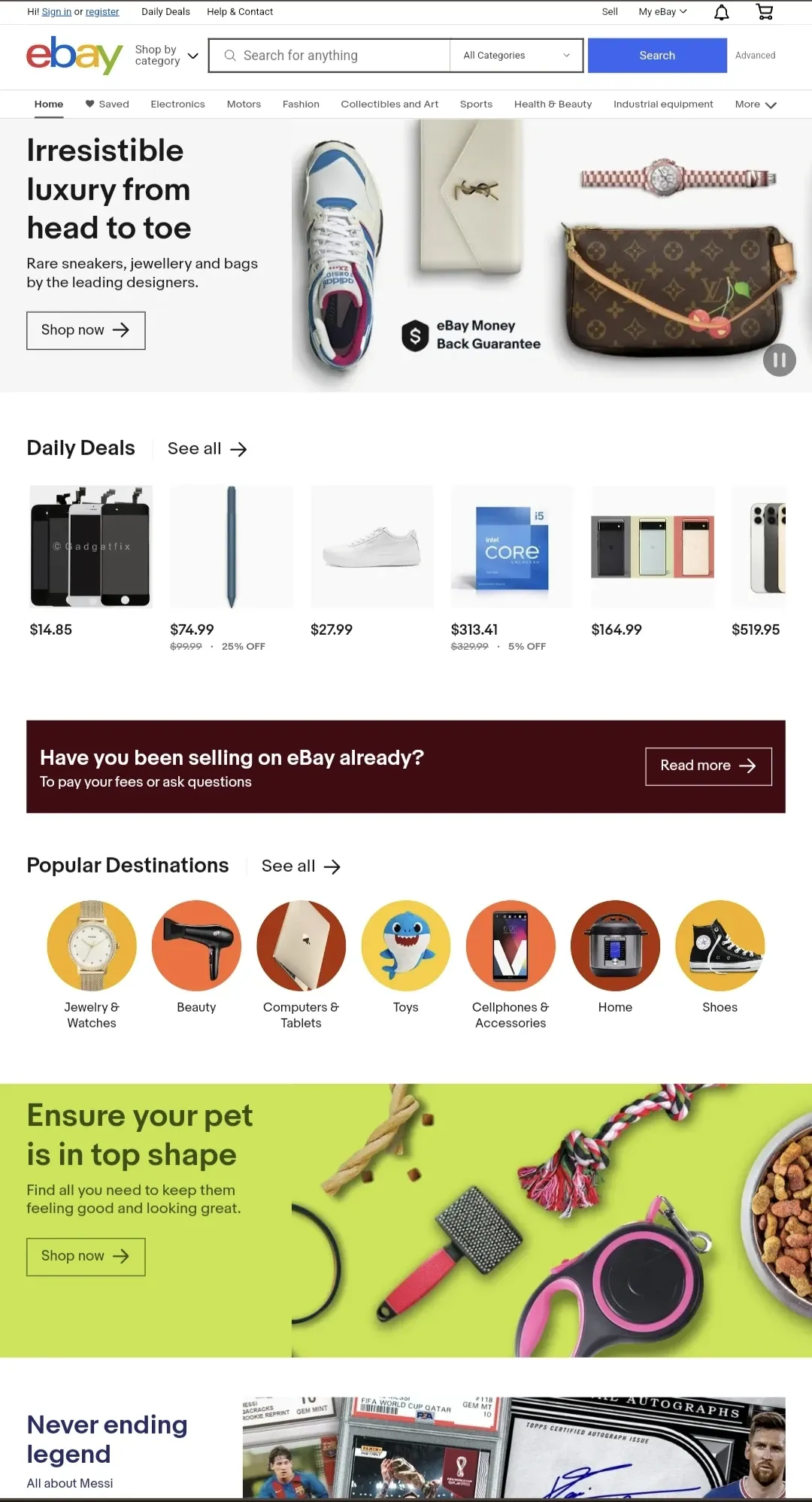
ecommerce business models-C2C-ebay
C2C is an ecommerce business model where consumers sell to another consumer.
Think of the eBay platform where a consumer can set up a shop and can sell products. The C2C business model of ecommerce is valuable to those consumers where another consumer no longer finds the need for one product.
The business model can be used to sell personalized or customized products which other retailers cannot replicate.
C2B
As the name suggests, Consumer-to-business is where the consumer offers a service or a product to a business. It’s like a marketplace where roles have been reversed – consumers set their terms and invite businesses to collaborate with them!
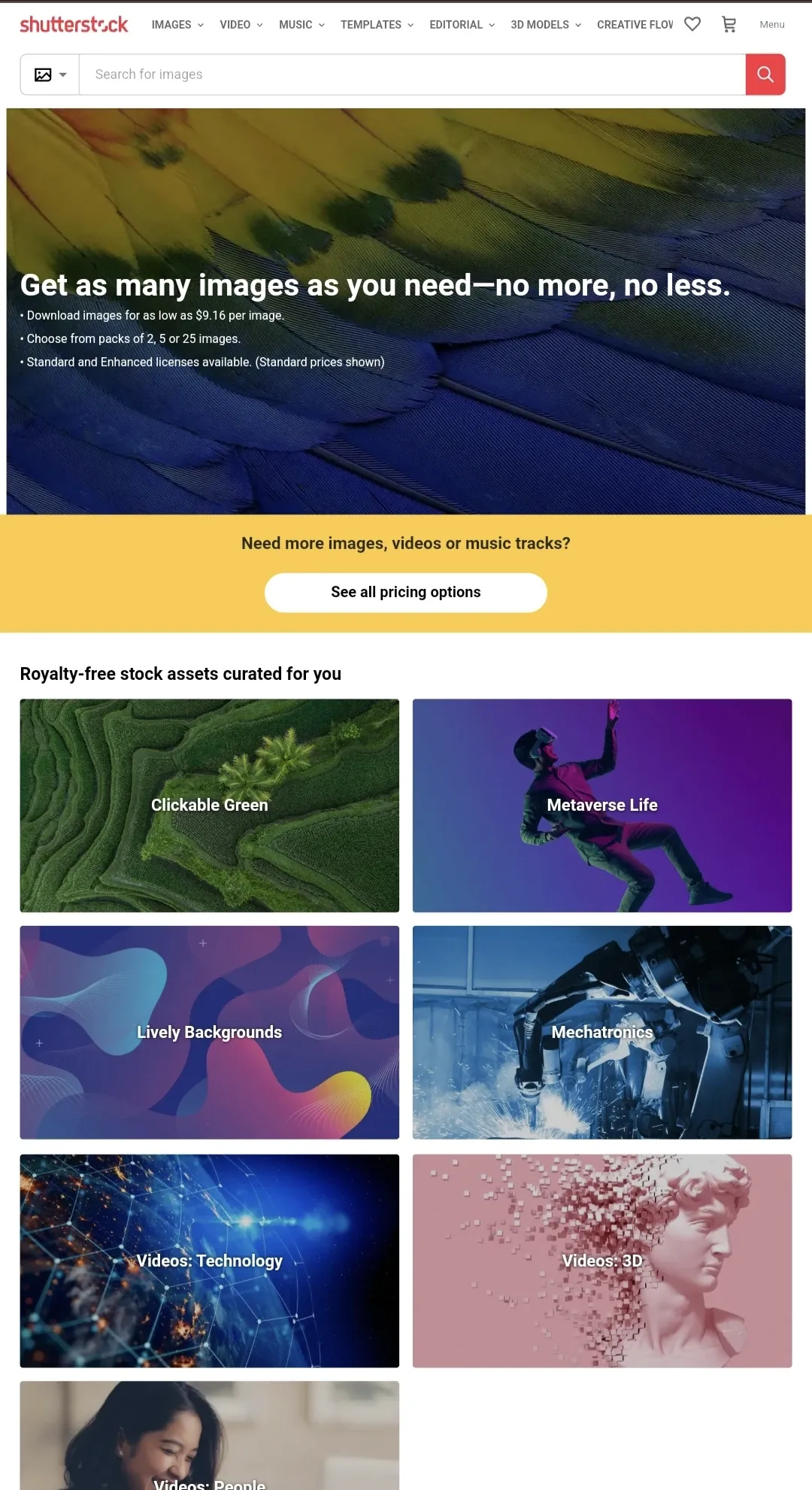
ecommerce business models-C2B-shutterstock
An example of a C2C business model is ShutterStock. A platform with a collection of photos, allows businesses to utilize the images uploaded by the consumers in exchange for a credit.
The C2C model is a right fit when a consumer has value to offer to the business. This value can be defined as freelance work, an influencer with a large follower base, YouTuber with a own brand, or any such value that aids a business in taking your service to uplift or promote themselves.
D2C
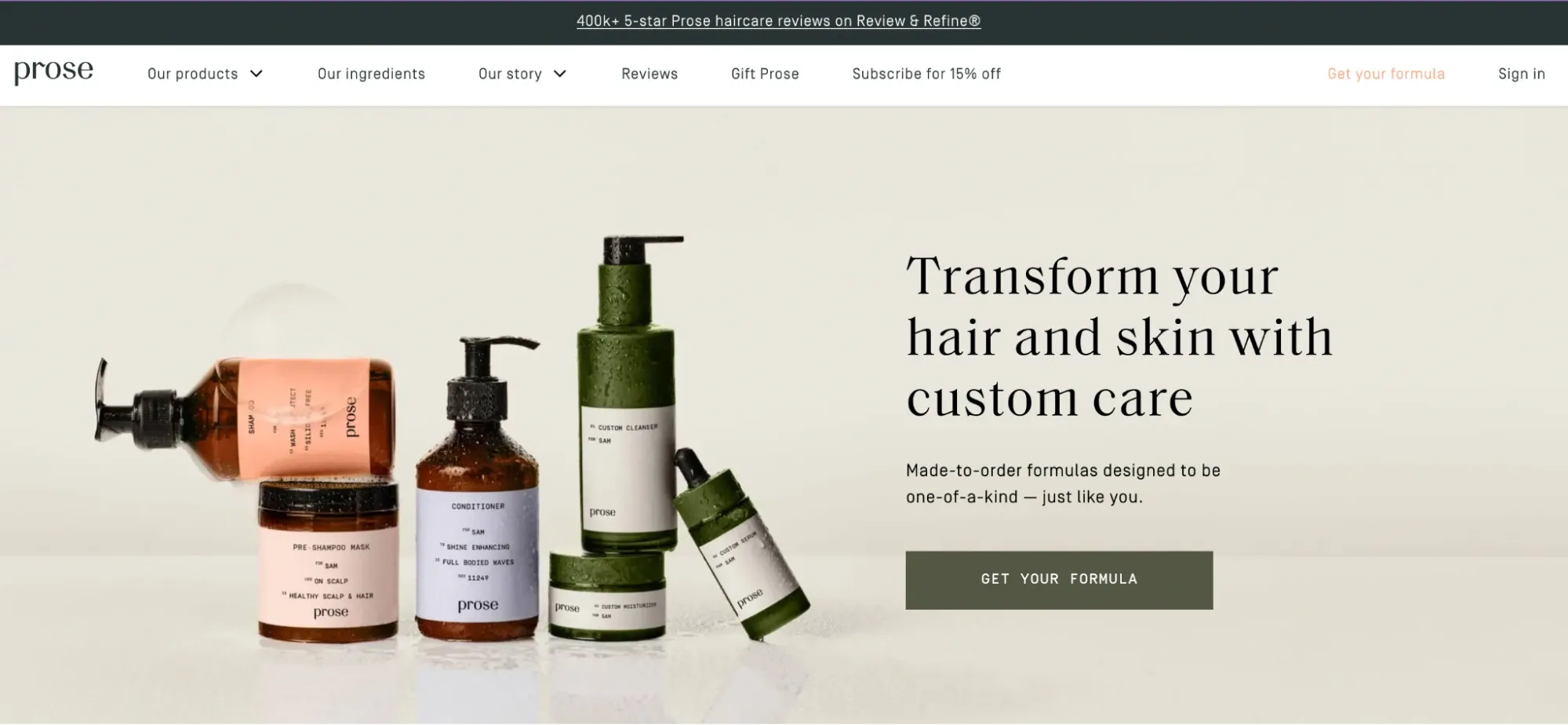
D2C ecommerce model stands for Direct to Consumers, meaning your brand sells the product directly to the customer online. You get the advantage of having your own customer base rather than having a customer base of retailers.
For example, Prose is a clean beauty D2C brand that sells its products through the online storefront.
ecommerce business models-D2C-prose
B2B2C
B2B2C stands for Business-to-Business-to-Consumer. The model emphasizes on businesses complementing each other with the services given to the same end user.
ecommerce business models-B2B2c-playstore
GooglePlay is the best example of a B2B2C model. As we are aware this marketplace for apps serves as an ecommerce business to the consumers of the apps developed by other businesses who are the suppliers of the app.
The ecommerce business model makes sense for manufacturing startups to leverage the user base of the ecommerce channel of the other business. It allows them to cut down on the cost of having their own model setup that the other business offers to still be able to serve the end user. That way you only agree upon giving certain commission to the other business rather than having the entire setup of distribution.
How to choose the right ecommerce business model?
Understand your audience
As an ecommerce entrepreneur, identifying who your potential customers are, is an important first step. It includes segmenting your target demographic by age, gender, location, income level, education level, and occupation, and psychographic segmentation like interests, hobbies, values, and lifestyles.
The next step is to understand shopping patterns and behaviors.
- How do they shop online and what motivates them to place an order?
- How are they feeling about the shopping experience?
Especially for business models in emerging ecommerce areas that matters because younger audiences may value fast, mobile-optimized platforms, while older consumers prioritize clear information and customer service over everything else!
What problem are you solving?
Understanding the problem you’re solving for your customers is important when deciding on an ecommerce business model. Your company’s value proposition is tied to the problems that a company solves for its consumers and the business model should align with this.
Identifying the problems involves research. You can collect important data points by conducting surveys and performing competitor analysis.
The thought process would involve answering questions such as;
- What are the potential challenges that your customers commonly face?
- How exactly are your products aiding your consumers?
- Is there a viable gap in the market that your business will fill?
- Is the problem significant enough for customers to pay for a solution?
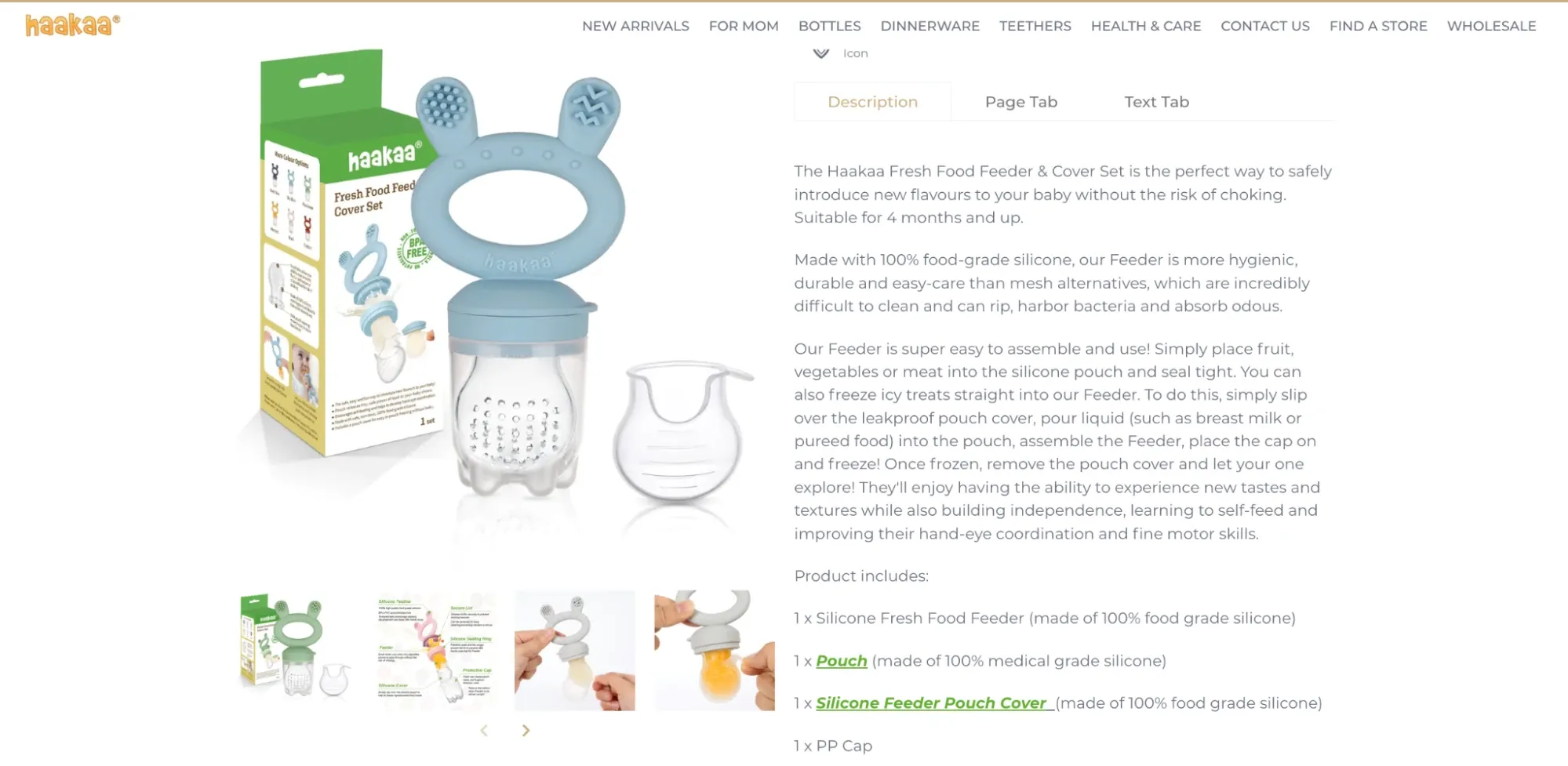
Haakaa is a D2C brand that sells silicone breast pumps to the target audiences. Its copy highlights the key value propositions: electric-free, 100% food-grade silicone, and easy to assemble and use. A quick look at the brand’s website shows that it understands the problems of the target audience (new mothers).
ecommerce business model-problem solving-Haakaa
Revenue model
The selection of the revenue model depends on the type of product and the audience that you are reaching.
Directly selling to customers is the most common way to generate revenue. Whereas a subscription model can aid in making recurring revenue in exchange for services or products for a subscription fee.
The different pricing strategies for ecommerce business model examples are:
1) Competitor pricing
The pricing strategy is based on tracking the prices of the competitors for similar products and considering an average price to sell.
2) Cost based pricing
The business focussed strategy to find the optimum price adding the product cost, shipping cost, along with marketing cost and the marginal profit that you wish to achieve aids in the selling price.
3) Value based pricing
It utilizes both the cost based and competitor pricing to come with the price of the product that adds value to your customer. Value based pricing takes into account the lowest selling price of the product, the average selling price of the product. On a difference of which we obtain the profit potential.
4) Dynamic pricing
Also called a demand and supply strategy where you decrease the price when there is high competition and increase the price when there is high demand and the supply is low.
5) Bundle pricing
When a customer is looking out for a specific product, you can bundle the offering with another relevant product to increase the average order value while giving it at a slightly discounted price.
What is your positioning?
You might have the best product to sell but what is the point of having if it’s not marketed well? The positioning of your brand matters equally along with having a great product.
For example, add a clear copy listing the product features and benefits. Showcase the product in use with product videos. Have user generated content and reviews highlighting how the product solves their challenges. They also serve as social proof, building potential customers’ trust and confidence in your brand.
In a nutshell, your business-to-business marketing does not have to be fancy. Be authentic, backup your offerings with clear copy and good-quality visuals, and add social proof.
Supply chain and logistics
So who are the suppliers, how is the order shipped and delivered? How to optimize the time gap between the order and the delivery with the team of operations? These are some of the aspects the businesses need to look into.
The supply chain comes with 6 stages
a) Supply and demand
The supply and demand in the market give an outlook on the pricing of the products. Supply and demand are rarely in equilibrium, and these fluctuations are crucial to respond to fulfill customer orders.
b) Warehousing
The place where the products are received, stored, and distributed. Without smooth warehouse management, there isn’t a smooth operation. And it is essential for the ecommerce businesses to handle the process efficiently.
c) Inventory tracking
Managing inventory is another step that is of great importance to your ecommerce company: be it B2C ecommerce business model or B2B ecommerce business model. The stocks in the inventory must be filled with the right products and in quantities. In order to meet all the orders on time, tracking the inventory implies that you have the products available at any point in time, cut down on excess items, and reduce over-selling.
d) Order entry
It is an entry in the record of order handling system for the retailers to schedule the activities to fulfill the particular order on time. Allowing both the store and the customer to be in line with the status of the deliverables.
e) Order management
At all stages of the supply chain, order management helps in coordinating with the process of order fulfillment.
f) Distribution, delivery, and returns
Distribution acts upon the warehousing and packaging of an item. Distribution is focused on the movement of the products from the supplier to the customer. Whereas the returns is a reverse management that tracks the order from the customer to the seller.
Marketplace vs single vendor
If you are a single vendor, it means you are the only one catering to multiple customers. In such instances, the stores usually have limited products to offer.
The multiple vendors are more like having a group of sellers in a marketplace selling to multiple customers and indeed having a vast range of products to cater to.
What is more important to understand here is the number of supplies that get involved in each type.
Having a good relationship with one supplier can be more reliable than having to handle multiple suppliers. And with huge volumes, they can reduce the cost of the product while dealing with a single vendor.
On the contrary, multiple vendors can turn out to be a savior when one supplier falls back though it might be difficult to handle and run a smooth operation amongst multiple suppliers.
Growth and scalability
Ever wondered how downtime can impact your profitability?
If you think it doesn’t really matter much, then you might be wrong!
When Amazon launched Amazon Prime, it had to engage its 100 million Prime members with deals and discounts, the website couldn’t handle the online traffic and during the peak volumes, it faced a major issue that cost them to lose $1 million per minute transactions.
The question is that when you start initially, you expect to grow year on year and be profitable. When you know your website is gaining traction and the volume is increasing, it means the number of orders is also increasing, this indicates that your website must be up for taking the traffic it demands and is well optimized for that situation.
Investment and resources
So what and all should be kept in mind before you start with one? The upfront cost of creating your platform includes development, design, and technology infrastructure for your website. Besides domain registration, website hosting, security measures, and payment gateways.
Utilizing marketing tools such as Lifesight’s Campaign Optimization can significantly enhance your platform’s growth by taking personalization to new heights, ultimately elevating the overall customer experience.
- Engage empowers you to make data-driven decisions for customer retention and personalization at scale.
- By analyzing real-time click data, tracking visits, and monitoring expenditures on emails, SMS, and other channels, Engage provides comprehensive insights into user behavior and engagement.
Set aside the budget for ongoing expenses such as advertising campaigns, marketing, software subscriptions, and website maintenance.
On the other hand, you need resources to handle the operations, all of this has to be estimated beforehand to seek sustainable growth with the ecommerce business model.
Importance of choosing the right ecommerce business model
Are you stuck with choosing the right ecommerce model? Here are the things to think about before selecting one.
- What product are you planning to sell?
- Begin by understanding your audience and focusing on their needs.
- What specific problems are you solving for them?
- What type of revenue model makes the most sense for your company?
- How are you positioning your brand in the market?
- What is the approach to marketing and customer reach?
- What is supply chain logistics?
- Will you be trying up with a single vendor or be in a marketplace?
- How are you seeing your business model from a growth and scalability standpoint?
- How much investment is required and what are the tools you need to run the ecommerce business model?
It is important to remember that the ‘right’ ecommerce model differs for each individual product and business!
FAQs
1) What are the most common 4 types of business models in Ecommerce?
The 4 common ecommerce business models are:
- Business to Customer (B2C)
- Business to Business (B2B)
- Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) or peer-to-peer (P2P)
- Consumer-to-business (C2B)
2) Which tools do you need to support the ecommerce business model?
The tools supporting ecommerce business model are:
- Marketing – MailChimp
- Analytics – Google Analytics
- Sales & Logistics – Shipwire
- Customer Service – Zendesk
- Communication – Slack
- Content Creation – WordPress
3) How to design my ecommerce business model?
Keep these things in mind while designing an ecommerce business model:
- Define your value proposition
- Identify your target market
- Choose a product or service offering
- Select an ecommerce platform
- Determine your revenue model
- Plan your marketing strategy
- Define your supply chain and logistics
- Focus on user experience
- Consider customer support and engagement
- Analyze and adapt
You may also like
Essential resources for your success