In 2023, businesses alone witnessed a staggering $100 billion in media spending evaporate due to inadequate measurement practices. As we move into 2024, the significance of marketing measurement becomes even clearer. It is not only a strategic necessity but also a crucial tool in navigating through a sea of data and channels.
This article aims to outline the evolution and predict key trends that will define marketing measurement in 2024. Drawing on the latest industry insights and our expert analysis, we aim to offer a roadmap for marketers seeking to optimize their campaigns and prove ROI in the new norms of a privacy-first, AI-driven marketplace.
Trend 1: Shift from Third-party to First-party Data
Marketers are now operating in a post-cookie world, where the use of first-party data and privacy-compliant methods has become the gold standard. This evolution is not just a response to regulatory pressures; it reflects a maturing industry that prioritizes consumer trust and transparent data stewardship.
Not long ago, marketers heavily relied on data from external platforms to understand customer behaviors and preferences. This data, often collected without direct interaction with the consumer, has been essential for creating personalized marketing campaigns. Nevertheless, this approach is changing rapidly.
A recent report by Twilio indicated that 43% of business leaders are already shifting their focus towards first-party data due to its capacity to deliver better privacy protections for customers.
This direct data comes from interactions such as website visits, app usage, or email engagement, and is voluntarily provided by customers. With this data in hand, marketers can tailor experiences more effectively, enhancing customer satisfaction and trust. Moreover, first-party data respects user privacy, aligning with the increasing global demands for data protection.
Adapting to this new norm requires robust systems like Customer Data Platforms (CDP) that can handle the complexities of gathering and utilizing first-party data. They help organize customer information from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of the customer journey.
Another compelling case for this shift is the success story of Domino’s Mexico, which, upon implementing a Customer Data Platform (CDP) to manage first-party data, saw a 65% decrease in cost per acquisition and a 700% increase in return on ad spending. This underscores the tangible benefits that first-party data management can bring to businesses in terms of efficiency and effectiveness.
These statistics not only illustrate the urgency with which companies are approaching the shift but also the benefits they stand to gain.
Trend 2: Rise of Unified Marketing Measurement Platforms
With the dawn of 2024, the marketing industry is undergoing a revolutionary shift towards Unified Marketing Measurement (UMM) platforms. This shift is monumental because it represents the merging of several attribution methodologies into a single, cohesive framework.
Rise of Unified Marketing Measurement Platforms
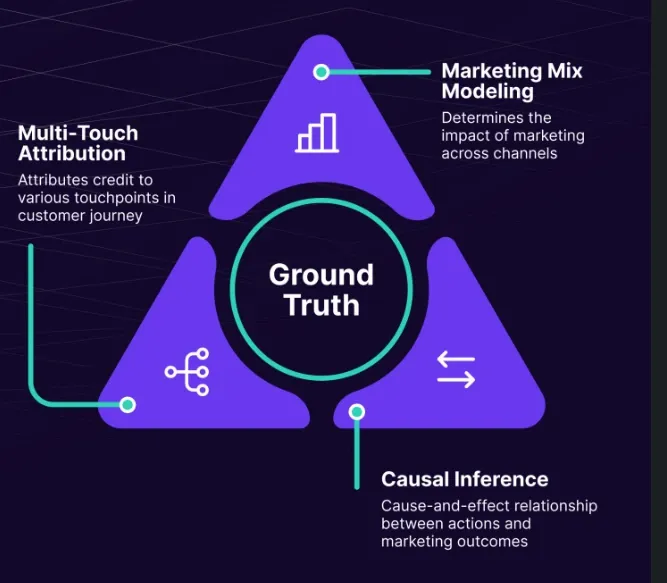
Unified Marketing Measurement (UMM) is a comprehensive approach that combines the robustness of marketing mix modeling (MMM), the precision of multi-touch attribution (MTA), the clarity of incrementality experiments, and the predictive power of causal AI to provide a comprehensive view of marketing efforts.
Now, let’s analyze the objectives, requirements, strengths, and weaknesses of these measurement approaches.
| Methodology | Objective | Required Data | Strengths | Weaknesses |
| MTA (Multi-Touch Attribution) | Day-to-day optimization of online campaigns and tactical adjustments. | Granular user-level data from digital touchpoints. | Near real-time performance tracking and allocation of value to customer interactions. | Often lacks offline media insights and may require third-party cookies. |
| MMM (Marketing Mix Modeling) | Strategic allocation across channels for budget planning and assessing marketing’s overall impact. | Aggregated KPI and media data on a weekly/daily basis. | Accounts for external factors and measures all media activities holistically. | Can lack the granularity needed for digital optimization and typically has a delayed feedback loop. |
| Incrementality Testing | Determining the incremental impact of marketing campaigns or creatives. | Detailed data from controlled experiments. | Highly detailed and accurate measurement with clear causal links. | Requires extensive planning, time, and resources; influenced by experimental design and external factors. |
| Causal Inference | Strategic decision-making is based on understanding causal relationships to predict outcomes. | All available data from digital and non-digital sources, experiments, and existing analyses. | Offers predictive insights into marketing outcomes and can operate without the need for direct experiments. | A complex implementation may require a sophisticated understanding of AI models. |
Trend 3: Increased Transparency in Measurement
This trend is gaining momentum due to the necessity for brands to establish trust with consumers and to navigate the complexities of a fragmented media environment with increased confidence. Stringent data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA have acted as catalysts, reinforcing the importance of transparency. These regulations require marketers to communicate clearly with consumers about data usage, which in turn affects the measurement tools and strategies they employ.
Brands are now more aware of the ethical implications of their data practices, leading to a shift towards using more transparent measurement platforms.
The enhanced transparency in measurement is directly connected to improved marketing effectiveness. When marketers understand the ‘why’ and ‘how’ behind the numbers, they can make more informed decisions that lead to better outcomes.
Trend 4: Privacy-First Approach: Shifting from Deterministic to Probabilistic Measurement
The fourth crucial trend in marketing measurement for 2024 is the definitive shift from deterministic to probabilistic measurement models. This change is driven by a privacy-first approach that has become paramount in the industry.
The adoption of a privacy-first strategy has accelerated due to increased consumer awareness and the implementation of strict privacy laws worldwide. In response, marketers are increasingly moving away from deterministic methods, which rely on specific and identifiable user data, toward probabilistic approaches that prioritize user anonymity and data protection.
Probabilistic measurement utilizes algorithms and statistical models to estimate the probability of marketing touchpoints influencing consumer behavior. Unlike deterministic methods that track direct interactions using identifiable data, probabilistic models aggregate data patterns to make informed predictions, thereby preserving user privacy.
This trend emphasizes the balance between maintaining measurement accuracy and respecting user privacy. Probabilistic models have advanced to the point where they can provide insights that are almost as precise as deterministic models, without compromising the privacy of individual data.
With the phase-out of third-party cookies and identifiers, the marketing world is adapting to a future without cookies. Probabilistic measurement is well-suited to this new reality because it does not depend on cookies to track user behavior across the web.
While the shift brings numerous benefits, it also presents challenges, such as the need for larger data sets and more sophisticated analysis techniques. Furthermore, the industry must continue to educate stakeholders about the value and effectiveness of probabilistic models to gain wider acceptance.
Trend 5: Rise of an Experimentation Culture
This trend indicates a significant change in how businesses approach marketing strategies, emphasizing learning and adapting through continuous testing.
Marketers are increasingly embracing an experimental mindset, where the “test and learn” approach becomes essential to the development of marketing strategies. This culture of experimentation is rooted in the scientific method, relying on hypotheses, controlled tests, and measurable outcomes to guide decisions.
Experimentation fuels innovation by enabling marketers to test new tactics on a smaller scale before implementing them widely. This approach not only mitigates risk but also encourages creativity. Marketers are less constrained by the fear of failure and more motivated by the potential for discovery and improvement.
Central to the culture of experimentation is the use of incrementality tests and A/B testing frameworks. These methods provide clear insights into effective strategies by comparing the performance of various marketing tactics against a control group.
The rise of an experimentation culture solidifies a data-driven decision-making ethos, where the abundance of data gathered from experiments informs and enhances marketing strategies, resulting in campaigns that are not only effective but also highly efficient.
Bonus trend: Causal AI-based decision-making
The causal AI market is anticipated to reach a value of $543.73 million, with the rise of research and development (R&D) activities being a key factor in this expansion.
Many prominent companies are pouring resources into Causal AI, including Uber, McKinsey, and Netflix. Causal AI was included in the latest Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies by industry analysis firm Gartner.
Why?
Because Causal AI helps businesses make more informed decisions. Instead of guessing or assuming the reasons why a marketing campaign worked well, Causal AI can determine the actual causes behind its success. This means that businesses can focus on what truly matters and make decisions that result in better outcomes.
For example, if a company observes an increase in sales following a specific ad campaign, Causal AI can assist in determining whether the campaign directly caused the increase or if other factors were involved. This deep understanding can guide them in planning their next steps.
Causal AI can predict the consequences of different choices before they are made. This is like having the ability to see into the future. Companies can utilize it to experiment with ideas in the virtual world, anticipate potential outcomes, and then select the optimal choice.
Typically, businesses must conduct real-world tests to determine the viability of their strategies, a process that can be both risky and costly. However, with Causal AI, they can conduct these tests in a simulated environment, which can save a significant amount of time and money.
All of this means that businesses can plan more effectively. They can have more confidence in their strategies because they are based on a clearer understanding of cause and effect.
Final Thoughts
As we move forward, marketers must embrace these new measurement methods. They offer a pathway to more effective, responsible, and customer-centric marketing strategies. With Lifesight, you gain access to advanced analytics, privacy-compliant data handling, and a suite of tools that are in line with the latest trends in marketing measurement.
Update: You can refer to key marketing measurement stats for 2024 and marketing measurement predictions for 2025 to further enhance your strategy for the coming year.
Book a demo now!
You may also like
Essential resources for your success