Marketing success today is defined not just by creativity and reach but by accountability and results. Marketers are increasingly expected to prove how their efforts directly impact business outcomes such as revenue growth, customer acquisition, and profitability. This makes marketing measurement a critical function, not a nice-to-have but a must-have. It enables teams to understand what is working, identify inefficiencies, and make informed decisions that drive performance.
By tracking key metrics like ROAS, CAC, and CLTV, and leveraging advanced models like Causal Marketing Mix Modeling, Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution, marketers can align strategy with measurable goals, optimize investments, and scale campaigns with greater confidence and clarity.
This guide explores what marketing measurement is, why it matters, how it works, the challenges it addresses, and how automation and unified marketing measurement frameworks can transform it into a powerful decision-making engine.
What is Marketing Measurement?
Marketing measurement is the process of evaluating the effectiveness of marketing efforts by collecting and analyzing data from both digital and offline campaigns across various channels to assess performance and support effective decision-making, such as budget allocation, spend optimization, campaign optimization, revenue forecasting, and new channel launch.
It involves tracking modern marketing KPIs such as ROAS, ROMI, CAC, iCAC, mROAS, CPL, iCPL, forecasted revenue, and measured lift to evaluate the results of existing campaigns, plan future marketing investments, and improve overall business performance.
Read About: Content Marketing Measurement, Digital Marketing Measurement and B2B Marketing Measurement
What is the Importance of Marketing Measurement?
Marketing measurement is important to understand the impact of marketing campaigns strategies to optimize the future campaigns based on the quantified results of existing campaigns. The data provides which strategies worked for which campaigns and channels and what’s the impact of revenue in terms of your strategies. It also helps you understand ineffective marketing strategies, channels and resources.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
1. Identifying successful marketing efforts
Measurement helps pinpoint which campaigns or tactics led to positive outcomes such as increased leads, conversions, or customer engagement, allowing you to replicate and scale them.
2. Identifying successful channels
It shows which marketing channels (e.g., email, social media, paid ads) are most effective in reaching and converting your audience, so you can focus efforts where they yield the best results.
3. Budget allocation
By knowing what works and what doesn’t, you can allocate your marketing budget more efficiently, directing funds to high-performing channels and initiatives.
4. Optimizing the spend level
Marketing measurement enables you to determine the optimal level of spend required to achieve desired outcomes without overspending or underspending.
5. Campaign optimization
Real-time or periodic performance data allows for ongoing improvements and adjustments to live campaigns to enhance results.
6. Identifying new channel opportunities
Measurement can uncover emerging or underutilized channels that show potential, enabling you to test and adopt new strategies early.
7. Forecasting and predicting the revenue
With historical data, you can build models to predict future campaign performance and revenue outcomes, aiding strategic planning.
8. Justifying marketing investments
Clear, data-backed evidence of performance helps justify marketing spend to stakeholders and secures future budget approvals.
9. Eliminating the wasted Ad spend and resources
By identifying low-performing campaigns or channels, you can cut back on wasted spend and reallocate resources to areas that deliver ROI.
Read Here About: Marketing measurement framework
What are the Top Challenges in Marketing Measurement Today?
Top marketing measurement challenges include data fragmentation and silos, difficulty in attributing value across channels, evolving privacy regulations across devices and browsers, keeping up with marketing measurement technological advancements, and achieving unified reporting and analysis.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
1. Data fragmentation and silos
Marketing data is often spread across multiple platforms, tools, and teams, making it difficult to consolidate and analyze holistically. This fragmentation leads to incomplete insights and hinders the ability to make data-driven decisions.
2. Attribution complexities across channels
Accurately assigning credit to the right marketing touchpoints in a customer journey is challenging, especially when interactions span multiple devices, platforms, and stages. Traditional models like last-click often fail to reflect true performance.
3. Growing privacy regulations
Evolving privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) and changes in browser tracking (like cookie deprecation) limit data collection and tracking capabilities, making it harder to measure user behavior and campaign impact accurately.
4. Lack of adapting to right measurement models
Many organizations continue to rely on outdated or overly simplistic measurement approaches, such as last-click attribution, which fails to account for the full customer journey. Not adopting a proper mix of modern models such as marketing mix modeling (MMM), causal attribution, and incrementality testing leads to misleading insights and suboptimal marketing decisions. These advanced methods provide a more accurate understanding of what truly drives performance across channels and touchpoints.
5. No unified marketing measurement analysis
Without a unified marketing measurement framework or platform, consolidating all marketing channels for consistent reporting becomes difficult. This prevents a clear and holistic view of performance across channels and campaigns.
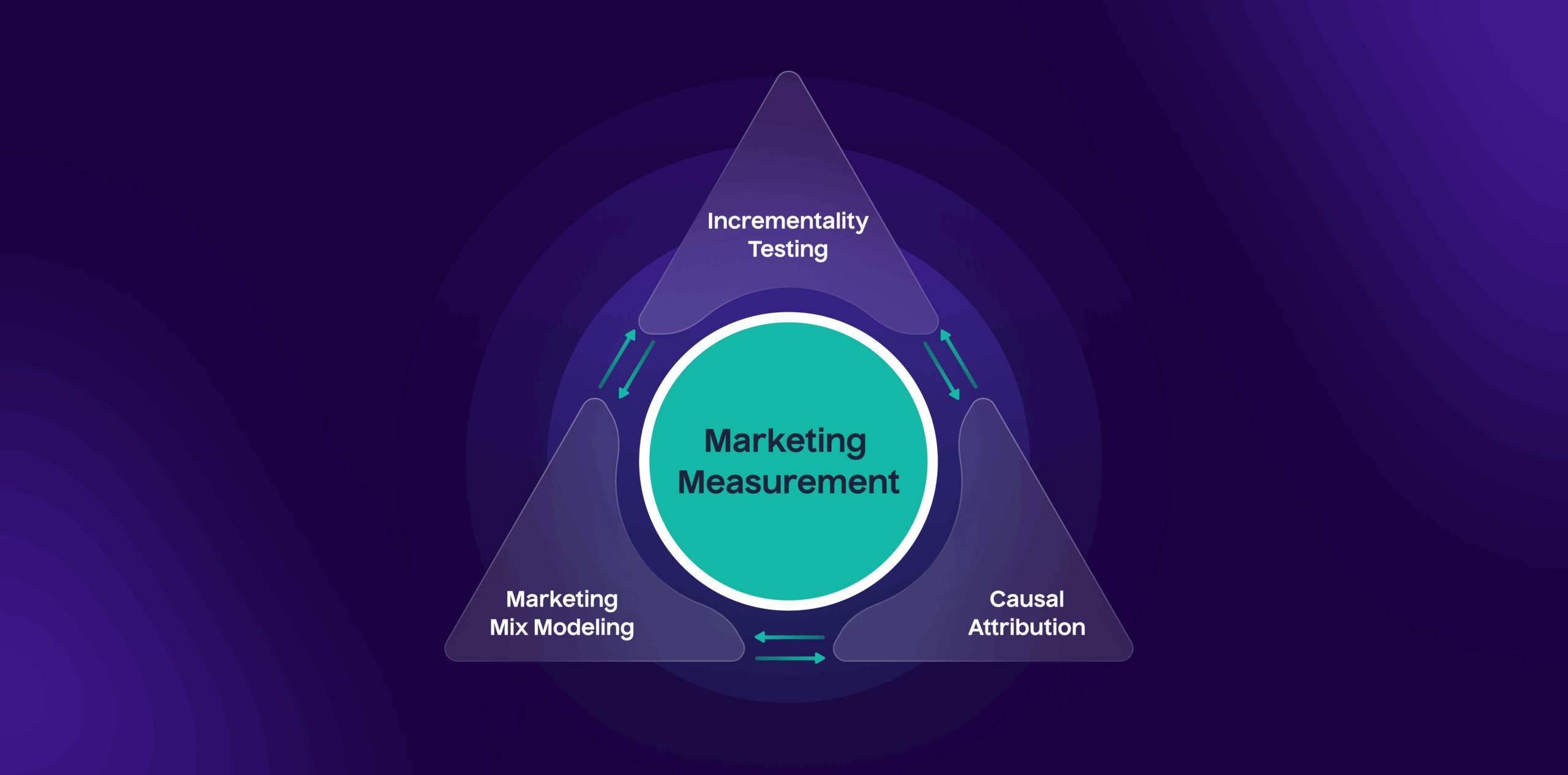
Advanced Marketing Measurement Models and Frameworks to Overcome those Hidden Challenges
1. Marketing mix modeling (MMM)
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) is a statistical analysis technique that evaluates the impact of various marketing and non-marketing factors on business outcomes like sales, revenue, or conversions. It typically uses historical, aggregated data over a long period.
MMM helps organizations understand how different marketing channels such as TV, radio, print, and digital, as well as external factors like seasonality, economic trends, and competitive activity, contribute to business performance. It allows marketers to quantify the return on investment (ROI) from each channel, identify diminishing returns, and optimize budget allocation across channels for maximum efficiency. Because it does not rely on user-level tracking, MMM is privacy-friendly and ideal for long-term strategic planning, especially in environments where customer-level data is limited or restricted.
2. Incrementality testing (Experiments / Lift studies)
Incrementality testing is an experimental method that measures the true effect of a marketing campaign by comparing outcomes between a test group exposed to the campaign and a control group that is not. These are often structured as A/B tests, holdout tests, or geo-based experiments.
This method determines whether a campaign actually caused a lift in conversions or sales, or whether those results would have occurred anyway. By isolating the direct impact of a specific marketing effort, it avoids over-attributing conversions to ads that did not influence behavior. Marketers can use this model to validate the effectiveness of channels such as paid social, display ads, or email campaigns. It is especially useful for budget justification and improving media efficiency. However, it requires careful experimental design and enough traffic or data to generate statistically significant results.
3. Causal attribution
Causal attribution is a data science-driven approach that uses statistical techniques and predictive modeling to determine the true cause-and-effect relationship between marketing activities and business outcomes, even without running controlled experiments.
Unlike simpler attribution models, causal attribution attempts to answer the question: “Did this marketing action cause the outcome, or would it have happened anyway?” It estimates counterfactuals, or what would have occurred without the marketing exposure, using methods such as propensity score matching, difference-in-differences, or Bayesian structural time series. Causal attribution is powerful for understanding effectiveness in complex, multi-touch environments where experiments are not always feasible. It enables marketers to simulate the potential impact of changing spend levels or reallocating budgets, supporting both tactical and strategic decisions.
4. Multi-touch attribution (Now considered limited)
Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) is a rule-based or algorithmic method that assigns proportional credit to each touchpoint in a consumer’s journey toward a conversion. It attempts to reflect the contribution of every interaction from the first impression to the final click.
MTA helps marketers analyze and optimize the user journey by showing how various touchpoints such as display ads, emails, or paid search clicks influence conversions. Models can be linear, time decay, or algorithmic depending on the distribution logic. While MTA offers valuable insights for campaign-level decisions, its effectiveness has declined due to growing data privacy restrictions, loss of cookies, and the inability to track users across devices and closed ecosystems. As a result, many organizations are moving away from MTA in favor of more robust and privacy-safe models.
5. Last-click attribution (Outdated)
Last-click attribution is the simplest form of marketing attribution where 100 percent of the conversion credit is given to the final touchpoint a user interacted with before converting.
This model focuses solely on the last marketing interaction, such as a Google ad click or a direct website visit. It is commonly used by default in many analytics and ad platforms because of its simplicity. However, it fails to account for the influence of earlier touchpoints like display impressions, social media engagement, or brand awareness campaigns. As a result, it often leads marketers to overinvest in lower-funnel tactics and underinvest in upper-funnel efforts that play a crucial role in influencing buyer behavior. While it is easy to implement, last-click attribution provides a highly incomplete and often misleading view of marketing performance.
Introducing Unified Marketing Measurement for Effective Marketing Measurement
As marketing becomes increasingly complex and fragmented across digital, offline, and cross-device channels, many organizations struggle to connect the dots between activity and impact. While advanced models such as Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution each offer valuable insights, they are often used in silos. This leads to fragmented analysis, conflicting signals, and an incomplete view of marketing’s true contribution.
Unified Marketing Measurement (UMM) is a modern, integrated framework that brings methodologies like Causal Marketing Mix Modeling, Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution together into a cohesive and comprehensive system. By combining the strengths of multiple models, UMM enables marketers to measure both short-term and long-term impact, link performance to revenue, and make confident, data-driven decisions.
This unified approach eliminates duplication, resolves measurement conflicts, and provides a single source of truth for marketing effectiveness. It ensures that your strategy remains aligned, accountable, and optimized for business growth.
How does Marketing Measurement Work with Advanced Measurement Models? A Step-By-Step Guide
Marketing measurement is the process of quantifying the success of marketing efforts by collecting, measuring, analyzing, and interpreting data to understand what’s working and what needs improvement. It involves setting clear goals, tracking relevant KPIs, and leveraging data-driven insights to optimize future marketing strategies.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
STEP 1. Define clear objectives
Start by aligning your marketing efforts with core business and revenue goals. Whether the aim is to drive qualified leads, increase customer lifetime value, accelerate sales pipeline velocity, or maximize return on marketing investment, clearly defined objectives ensure that every marketing activity is directly tied to measurable financial outcomes. This alignment sets the foundation for meaningful and accountable marketing measurement.
STEP 2. Identify key performance indicators (KPIs)
Select KPIs that directly reflect your revenue-focused objectives. For example, if the goal is to drive sales or improve ROI, prioritize metrics like return on ad spend (ROAS), customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLTV), and marketing-sourced revenue. If you’re focused on pipeline growth or lead quality, track metrics such as lead-to-opportunity conversion rate, average deal size, or sales velocity. The right KPIs ensure that marketing performance is measured in terms of its actual impact on business growth.
STEP 3. Gather data from various sources and channels
Collect data from all relevant marketing and sales platforms that contribute to your selected KPIs. This includes ad platforms (e.g., Google Ads, Meta), CRM systems (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot), web analytics tools (e.g., Google Analytics), email and automation platforms, and e-commerce or sales systems. Ensure that both online and offline channels are included where applicable. Consolidating this data enables a full view of how marketing activities contribute to pipeline, conversions, and revenue, forming the foundation for accurate measurement and attribution.
STEP 4. Choose right marketing measurement model
Select a measurement model that can accurately attribute marketing’s contribution to revenue outcomes. For high-level, strategic insight, use Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) to understand the impact of each channel on sales over time. For precision, apply Causal Attribution and Incrementality Testing to determine whether specific campaigns or tactics actually drive incremental revenue. Avoid outdated models like last-click attribution that misrepresent the customer journey and skew ROI analysis.
STEP 5. Monitor key metrics
Continuously track the KPIs defined earlier, such as ROAS, CAC, pipeline contribution, and CLTV, through real-time dashboards and automated reports. Monitoring these revenue-linked metrics ensures that performance is evaluated in financial terms and enables faster adjustments when campaigns are underperforming or overdelivering.
STEP 6. Adjust your campaigns based on data
Use insights from your metrics and models to fine-tune marketing strategies. Reallocate budget toward channels and campaigns that generate the highest return, improve targeting to attract higher-value customers, and eliminate spend on low-impact efforts. Optimization should always be guided by measurable gains in revenue or profit margin.
STEP 7. Test and experiment
Start with geo-based experiments, which involve splitting your target market by geographic regions to test the performance of a specific marketing tactic. For example, you might launch a new paid media campaign in one set of regions (test group) while withholding it from another comparable set (control group). By comparing revenue outcomes such as sales lift, average order value, or deal conversion rates between the two, you can isolate the true impact of the campaign without needing individual-level tracking.
STEP 8. Calibrate the model with new experimented data
Update and refine your measurement models using fresh data from experiments and actual revenue performance. This ensures your models stay relevant as market dynamics, buyer behavior, and channel effectiveness evolve. Ongoing calibration improves forecasting accuracy and enhances your ability to predict future revenue impact from marketing investments.
Modern Key Metrics and KPIs to Track Effective Marketing Measurement
- Cost per lead (CPL): Average cost to generate a lead.
- Incremental CPL (iCPL): Cost per lead driven exclusively by marketing beyond organic or baseline activity.
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC): Average cost to acquire one new customer.
- Incremental CAC (iCAC): Cost per net-new customer directly attributable to marketing.
- Conversion rate (CVR): The percentage of users who complete a desired action.
- Lead-to-customer conversion rate: Percentage of leads that convert into paying customers.
- Customer lifetime value (CLTV): Total projected revenue a customer will generate during their lifecycle with the brand.
- Incremental revenue: Revenue that would not have occurred without the specific marketing activity being measured.
- Measured lift: The percentage increase in conversions, leads, or revenue caused by a campaign. Typically obtained through A/B tests or geo-holdout studies.
- Marketing-attributed revenue: Total revenue generated or influenced by marketing efforts.
- Return on Ad spend (ROAS): Revenue earned for every dollar spent on advertising.
- Incremental ROAS (iROAS): Focuses only on the incremental revenue driven directly by marketing, often determined through experimentation or modeling.
- Measured ROAS (mROAS): ROAS validated through modeling techniques like Marketing Mix Modeling or causal attribution.
- Return on marketing investment (ROMI): Profitability measure that considers total marketing cost.
Marketing Measurement Automation
For marketers aiming to measure the effectiveness of their campaigns, there is no need to build a measurement framework entirely from scratch. Today’s marketing ecosystem offers automation capabilities that streamline the entire measurement process, from data collection to performance reporting, without requiring complex custom setups.
There are modern tools available that combine advanced methodologies such as Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution into a single, integrated solution known as a Unified Marketing Measurement platform. These platforms are designed to help marketers understand both short-term and long-term impact, isolate true lift, and identify what is genuinely driving conversions and revenue.
With marketing measurement automation, you can:
- Unify data across marketing and sales channels: Eliminate data silos by consolidating performance data from digital, offline, and CRM systems into one integrated view.
- Apply blended measurement models across campaigns and platforms: Leverage a combination of Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution to assess both short-term and long-term impact.
- Track real-time KPIs such as ROAS, CAC, CLTV, and conversion rates: Monitor the key metrics that tie marketing performance directly to business outcomes.
- Automate reporting and performance analysis: Generate consistent, on-demand insights across teams and stakeholders without manual reporting.
- Run controlled experiments and validate incremental impact at scale: Execute A/B tests, holdout studies, or geo-split tests to measure true campaign lift and improve decision confidence.
- Enable accurate budget allocation and channel investment decisions: Allocate marketing spend more efficiently by understanding which channels, campaigns, or audience segments deliver the highest return.
- Determine optimal spend levels for each channel or tactic: Use diminishing returns curves and performance modeling to identify how much to invest in each channel before performance starts to plateau.
- Forecast and predict revenue based on campaign inputs: Use historical and modeled data to estimate future outcomes and align marketing strategies with growth goals.
- Optimize campaigns in real time based on performance data: Quickly adjust creatives, messaging, budgets, and targeting to improve campaign effectiveness while in flight.
- Achieve unified reporting across teams and business units: Centralize measurement and ensure all stakeholders work from a consistent and reliable set of metrics.
- Support new channel launches with early measurement readiness: Apply test-and-learn strategies to evaluate the impact of emerging channels and decide when to scale them.
Automation improves speed, accuracy, and scalability. It enables marketers to spend less time managing data and more time optimizing performance and making strategic decisions grounded in measurable results.
Best Advanced Marketing Measurement Tools
Here’s the advanced marketing measurement tools which combine methodologies like Marketing Mix Modeling, Incrementality Testing and Causal Attribution.
Read More About: 10 Best Marketing Measurement Tools in 2025
Conclusion
Marketing measurement has evolved from basic tracking into a strategic capability that drives accountability, optimization, and growth. With increasing complexity across channels, privacy regulations, and the pressure to justify marketing spend, organizations can no longer rely on outdated or siloed models. Advanced approaches like Marketing Mix Modeling, Incrementality Testing, and Causal Attribution provide a more accurate, unified view of marketing’s true impact. By automating measurement and adopting a unified marketing measurement framework, marketers gain the clarity and agility needed to make smarter investment decisions, forecast outcomes, and accelerate business performance. Ultimately, effective measurement is not just about tracking results. It is about enabling marketing to become a strategic driver of business growth.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Marketing Analytics and Marketing Measurement?
Marketing analytics focuses on analyzing historical data and trends, while marketing measurement is about assessing the effectiveness of campaigns against specific goals. Measurement is outcome-driven and used for performance evaluation.
2. How do i know if my marketing efforts are successful?
Success is determined by tracking KPIs such as ROAS, CAC, CLTV, and conversion rates, and measuring them against your business objectives. Consistent ROI and incremental impact are key indicators of success.
3. What are the most common mistakes in marketing measurement?
Relying on last-click attribution, using siloed or incomplete data, ignoring incrementality, and failing to align metrics with business goals are common pitfalls. These lead to misleading insights and poor decisions.
4. How does customer journey impact marketing measurement?
The customer journey introduces complexity with multiple touchpoints across channels. Accurate measurement must account for this by using multi-touch or causal models to fairly attribute performance and influence.
5. How does comprehensive marketing measurement and optimization solutions work?
They integrate data from multiple channels, apply advanced models like MMM and attribution, and generate insights to evaluate performance. These solutions help optimize spend, forecast revenue, and guide real-time campaign adjustments.
Essential resources for your success