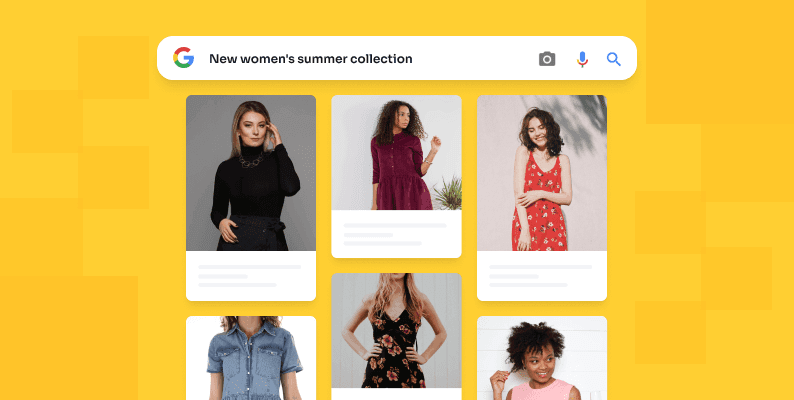
Guess the most important factor for dominating the ecommerce market, besides having superior products and service… Yes, appearing in the top positions of SERPs.

This is where ecommerce SEO comes into play. SEO for ecommerce addresses the initial barrier to acquiring new customers: driving traffic to your site. A few interesting facts:
- More thantwo-thirdsof all clicks on SERPs go to the top five results.
- 70%of marketing experts agree that SEO yields better results than PPC.
- 70–80%of Internet users ignore paid ads.
What is ecommerce SEO?
Ecommerce SEO is the process of increasing the visibility of your online store in search engine results pages (SERPs). When people search for products you sell, you want to rank as highly as possible to attract more visitors.
Ecommerce SEO typically entails optimizing your headlines, product descriptions, meta data, internal link structure, and navigational structure for search engine optimization and user experience.
Each product you sell should have its own page optimized to attract visitors from search engines. However, you should not overlook static, non-product-focused pages on your website, such as the following:
- Home page
- About page
- FAQs page
- Blog entries
- Help center answers
- Contact page
Create a list of keywords for these pages as well as a list of keywords with which they are associated.
Hot tip
For your specific DTC industry, let’s say beauty – study the website structure, site pages, page content, and keywords for which your competitors’ pages rank for. You’ll notice, many add product categories, or bundles on their homepage to contextually let the customer discover and give search engines more context about their website.
Why is SEO important for ecommerce websites?
If your website is absent from the SERPs, you lose access to qualified and interested customers. Your products may have an online presence, but are they discoverable?
This is where ecommerce SEO comes into play. It allows you to reach your target audience without paying for advertisements. Only if and when you have attracted visitors to your website, can you impress them with high-quality products, captivating copy, and compelling calls to action.
Yes, you can also acquire traffic through paid search, but SEO is much more cost-effective. In addition, ad blockers andad blindnesscan reduce the effectiveness of paid search, so you should optimize for search anyway.
High-level SEO strategy for ecommerce website
Before we move to the specific tips you can use to enhance ecommerce SEO, keep this high-level strategy in mind.
Implementing ecommerce SEO may seem like a daunting task, especially if your site sells a lot of products. Yes, it may take time, but you can accelerate the process with a sound plan:
- Prioritize pages: Determine which pages on your site receive the most traffic and prioritize them. Moreover, if you want customers to focus on a particular or flagship product, optimize for that product first.
- Create an SEO workflow: SEO requires that you fulfill numerous specific requirements: choosing keywords, adding meta data, correctly naming images, adding image alternate attributes, and incorporating related keywords.
- Analyze the competition: Your SEO strategy for ecommerce should be designed to outsmart the competition. Examine the sites of your leading competitors and evaluate their SEO efforts. Identify ways to improve yours.
- Continue with CRO: Conversion rate optimization (CRO) enhances your site’s shopping experience to increase a particular KPI, typically sales. Perform CRO on landing pages, category pages, or any other customer touchpoint. Making checkouts easier and faster, using advanced filters to help customers find products, and displaying returns and refund policies strategically are some of the examples of optimizing your site for conversion.
11 tips to enhance your ecommerce website SEO
1) Analyze the keyword search volume, CPC, and user intent to use the right keywords
Mention your primary keyword(s) in your product headline, description, meta description, image alternate attributes, and subheadlines.
Importantly perform research on a keyword before using it. Know how often people search for it (keyword search volume), how competitive it is in paid advertising (cost-per-click, or CPC), and what people are looking for when they use it.
Let’s discuss it further.
Search volume indicates the level of consumer interest in a particular keyword. A high search volume indicates greater popularity, which means that the keyword will receive more active searches.
The CPC indicates how much people pay per click when purchasing advertising based on a particular keyword. A high CPC indicates heightened levels of competition. Consider a long-tail alternative if the keyword you wish to target is extremely competitive.
User intent describes what people are looking for when they type a keyword into Google’s search bar. Suppose a customer types “shower” and then presses Enter, are they seeking information regarding shower installation, shower repair, baby showers, wedding showers, or something else entirely? Add additional words to the search string if you cannot determine the user intent behind a given keyword.
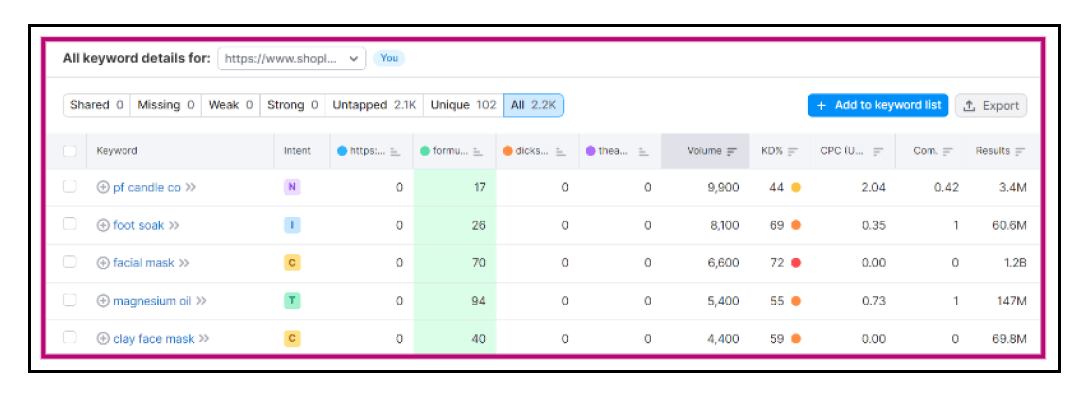
Semrush throws up these keywords for L’AMARUE based on user intent and search volume (vis a vis its competitors), for instance:
2) Remember to add LSI keywords
Sprinkle latent semantic index(LSI) keywords throughout your product pages. These are related keywords that help Google understand your product page(s) in context.
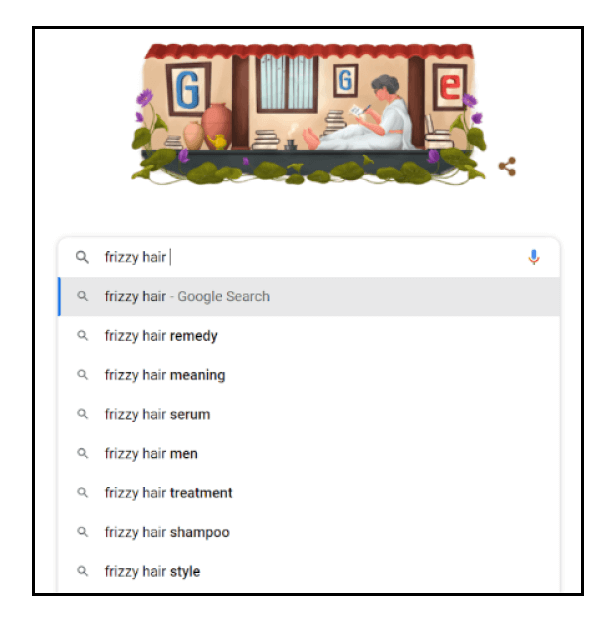
To help paint a picture, take the words “frizzy” and “hair care”. When separated, these words represent two very independent definitions, but when brought together, their formation creates a brand-new concept: “frizzy hair care”.
If you sell frizzy hair care shampoos, you don’t want your content arising for the word “frizzy” alone — in that case, you’d need to use LSI keywords to help let search engines know for which searches it should serve up your content:
3) Conduct competitor research
If you have no idea where to begin with on-site SEO optimization, your competitors are your best source of information. Your bigger competitors have likely already optimized their sites, and you can discover many of their secrets by visiting their sites.
Keywords should be your primary focus. Specifically, you should analyze the keywords on their homepages and leading product pages.
You can start by using the Moz browser extension to see the SEO title and description your competitors use in their title tags.
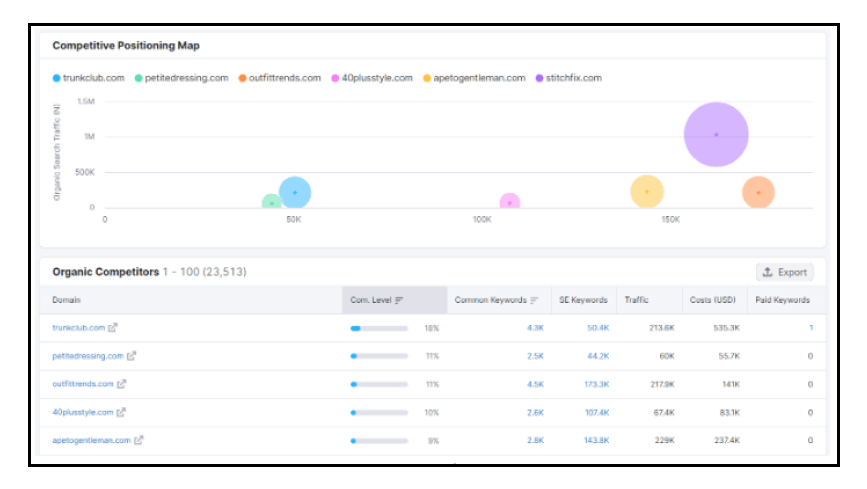
You can also use tools like SEMrush to determine which organic and paid keywords your competitors are ranking for. For instance, this is what the organic research on SEMrush displays for Stitchfix and their top 5 competitors:
Do not limit your research to keywords alone. Examine the landing pages of your competitors as well, so you can see how they optimize those pages with the specified keywords.
4) Focus on homepage SEO
The homepage is typically where the majority of SEO budget and effort is allocated. So, you should optimize your homepage for SEO effectively. The most important elements to add and optimize include the following:
Homepage title tag
The SEO title tag is one of the most crucial components of on-site search engine optimization. It should contain your brand/product name and the primary keyword phrase you’re targeting. This title tag should contain fewer than 70 characters and be appealing to search visitors, as it will appear in search engine results.
Home page meta description
While this is not important as far as keyword rankings are concerned, the meta description for your homepage is a 160-character description of your business that will also show up in search beneath the title tag. So, write it in a way that compels people to want to visit your website.
Burrow has optimized both the title tag and meta description really well as is evident here:

Homepage content
The content on your homepage should provide visitors with clear and concise information about your brand and its products. Avoid overwhelming visitors with excessive content. Consider featuring your top few products and your unique selling proposition on the homepage.
For instance, The Mountain has a simple navigation bar containing the primary product categories that encourage exploration. The hero slider features the most recent seasonal goods and promotions and encourages further exploration. With a wider variety of product categories, The Mountain has done an excellent job of categorizing everything to reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed that many ecommerce sites can cause:
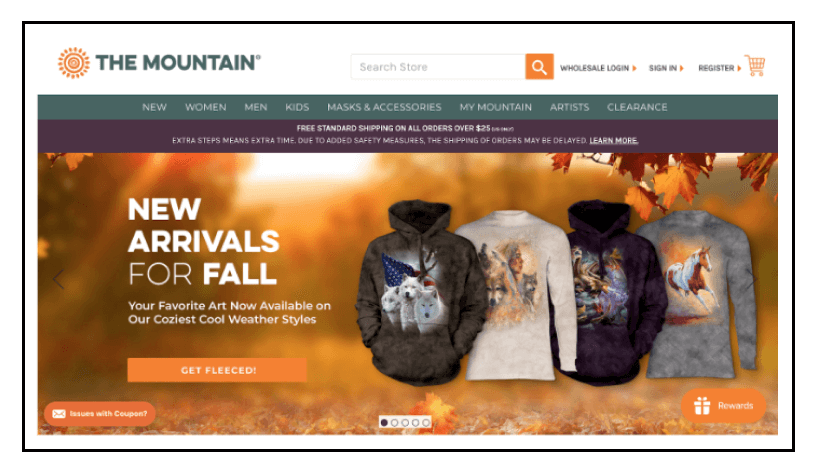
5) Simplify your site architecture
As you add more products and categories to your online store, keep in mind the importance of site architecture for SEO. You should have a distinct navigational hierarchy from your homepage to your product categories to the products listed within them.
Your site’s pages and products will be discovered by search engine bots if the internal linking structure is straightforward and shallow.
The rule of thumb for search engines and visitors/customers is to ensure that everything is accessible within three clicks. There should be no more than three clicks required from the homepage to reach any product on your website:
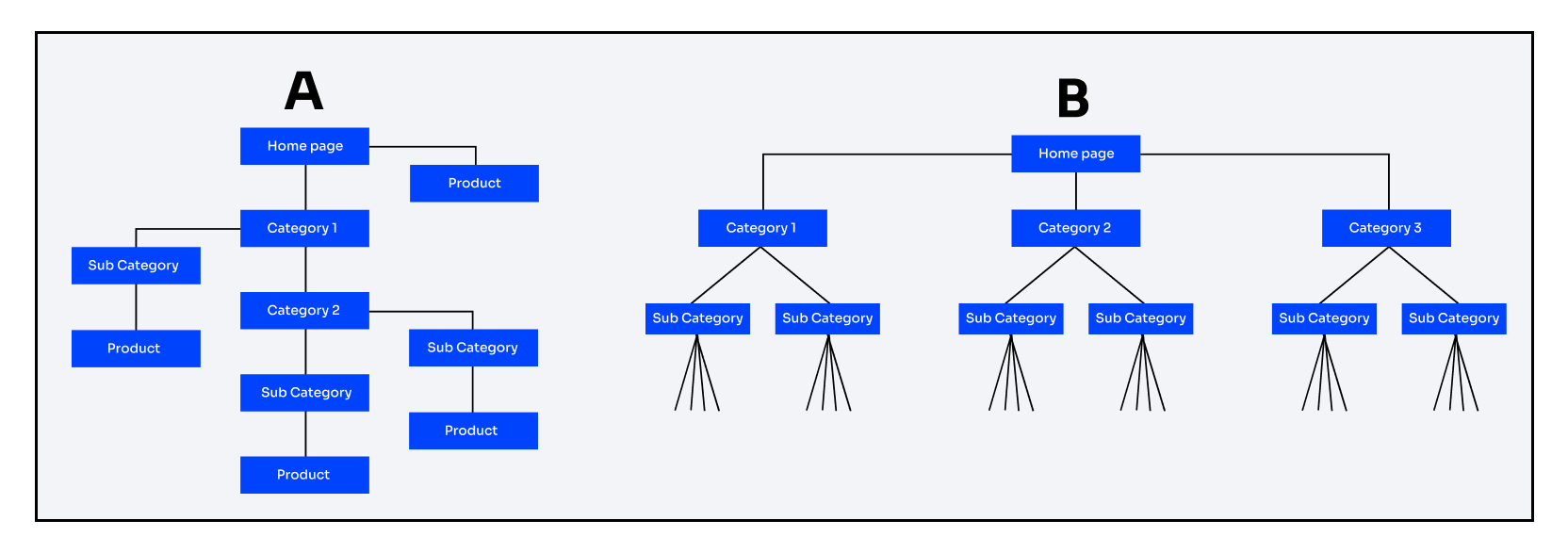
Observe Site A architecture: it is extremely complex and difficult to navigate. Due to its lack of scalability, you are required to analyze and organize the items each time you add new categories or products. And the most significant flaw is that, in deep site architecture, the authority passed by your site’s homepage is weakened until it reaches the product pages.
In the case of Site B architecture, the required page (product page) can be accessed within three or fewer clicks. It not only improves the user experience, but also ensures that product pages receive the appropriate authority from the homepage and makes it simpler for search engines to categorize and index the pages.
Internal linking
Internal links serve two principal functions:
- Boosting ecommerce SEO by displaying inter-page relationships
- Increasing site dwell time by encouraging visitors to explore further
Linking to related products or blog articles that are rich in information can improve ecommerce SEO and make your site more enticing for deeper exploration. For instance, Solo’s blogs provide internal links to their products in a non-intrusive way:

6) Optimize PDPs
Product Detail Pages (PDPs) are the lifeblood of your business, so you will need to devote a substantial amount of effort to their SEO optimization. Please don’t just include a few lines of text and an image or video for each product.
Google requires more information on your product pages to index them. Here are the specific objectives you wish to pursue:
Include product name in description
The product’s name is vitally important. In most cases, it is also used in the page’s SEO title and URL. Consider including a common search term or keyword phrase in your product descriptions.
For instance, include “T-shirt” or “tee” in the product name if you are selling t-shirts, for example. Thus, the keyword will also be included in the SEO title and URL:

Additionally, when people share your product on Facebook or Pinterest, the keyword will be included in the shared post’s title.
Optimize images
Images are a crucial component of your PDP. Consider your customer’s perspective for a moment. Are you more likely to purchase a product from a site that clearly depicts the product from as many angles as possible, a site with no image whatsoever, or a site with a small, illegible image?
Images are not only important for your customers, but also for search engine optimization.
To optimize your image files for search, begin with the filename. Do not include “IMG0010.jpg” images on your PDPs. Use the product name and primary keyword instead, such as “eastcoast-skinny-jeans.jpg”.
If you have alternative views of your product, you should include keywords that people would use to search for those images.
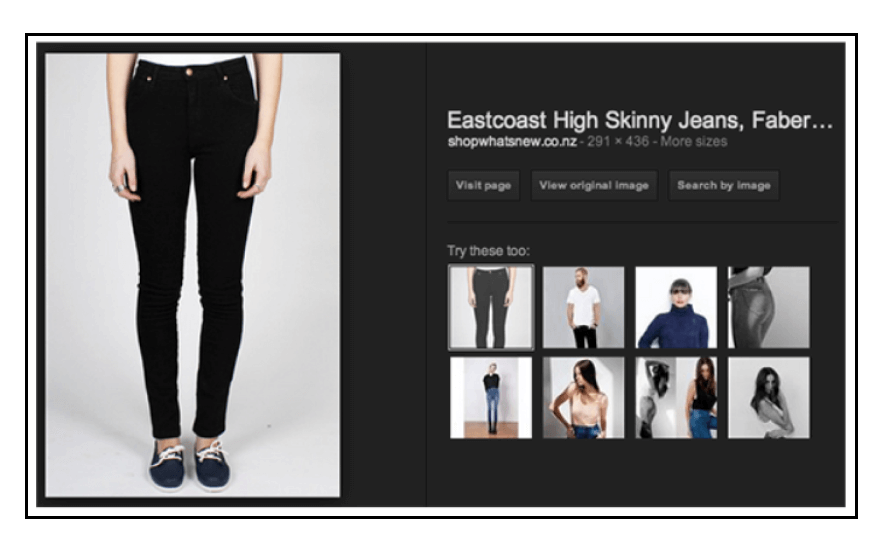
Also, when adding images to your product page, include the product name and a relevant keyword in the image’s ALT text.
The outcome? Your images may now appear in Google Image Search, as depicted in the image above.
Include videos, if possible
Add a video to your PDP to help your customers feel more assured about their purchases.
The video could contain basic information about your product (similar to a commercial), a tutorial on how to use the product to achieve results, and UGC such as unboxing videos or user reviews.
Publishing videos on networks such as YouTube (and linking them to your PDP) can be a fantastic way to attract and educate potential customers about your products.
Using your products’ DIY videos, for example, can demonstrate how to create something extraordinary quickly. Once they become interested in the project, they will be more likely to purchase your related products:
Add customer reviews
You should definitely display customer reviews on your PDPs. Visitors searching for product reviews should be able to quickly find honest reviews, which are rewarding and compelling enough for them to make the purchase.
Customer reviews provided on social media channels should also be linked/displayed on your PDP.
Include FAQs content
Do people ask questions about your products? Obviously, they do. Including product-specific FAQ content on your PDPs is essential for product discoverability and also for increasing conversions.
If customers have questions that you do not answer, they will go elsewhere to find the answers and will likely purchase from the source that does.
Include a general FAQs page on your site. Answering fundamental questions regarding your site’s security, shipping, and refund & return policies can boost brand discoverability, buyer confidence and increase sales.
Avoid duplicate content
Google will not like you if the PDP for your red socks is identical to the page for your blue socks. Eliminating duplicate content demonstrates to Google that your site is efficiently constructed.
Hot tip
Use product variants instead of creating brand new pages for color, size, and style variations of a product.
7) Locate and fix 404 errors
A 404 error occurs when a customer visits a webpage that does not exist. Google will not like you if people frequently land on a page that does not exist.
Using a tool such as brokenlinkchecker.com and removing the page or implementing a 301 redirect is the most effective method for locating and fixing 404 errors.
8) Use mobile-first indexing and design
Google’s mobile-first indexing uses mobile friendliness as a ranking signal.
The following mobile-first indexing best practices should be implemented on both the mobile and desktop versions of your site:
- Text, images (with alt attributes), and videos that are equivalent for mobile and desktop versions
- Structured data
- Title tags, meta descriptions, and other metadata
- Correct canonical tags
Ensure Smartphone Googlebot can access your pages.
9) Reduce page load speed
Page load speed is also a ranking signal, both for desktop and mobile. The faster your pages load, the better Google will rank you.
The average loading time for a first-page result on Google is 1.65 seconds.
As depicted in the image below, a Google studyindicates that the slower a mobile site loads, the greater the likelihood that a visitor will bounce:
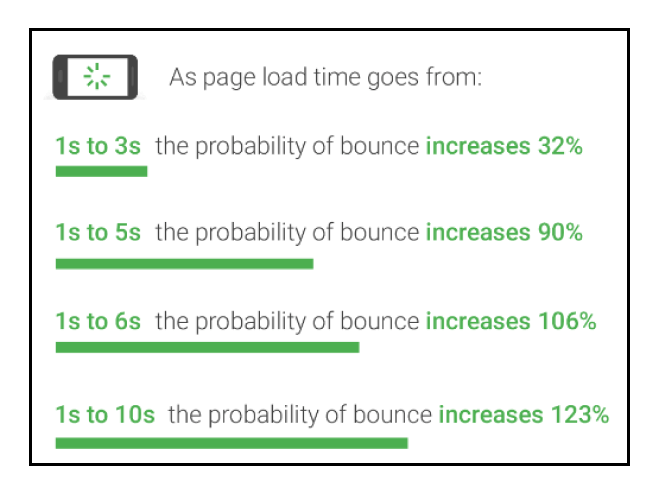
How do you decrease page load speed?
Focus on subtracting as many unnecessary elements from your page as possible. For instance, a huge background image that’s mostly covered by a white body column might not be necessary. Similarly, remove any plugins or add-ons that don’t contribute to your ecommerce business’s bottom line.
Google provides a checklist for optimizing page speed:
- Avoid landing page redirects.
- Enable compression.
- Improve server response time.
- Leverage browser caching.
- Minify resources.
- Optimize images.
- Optimize CSS delivery.
- Prioritize visible content.
- Remove render-blocking JavaScript.
Image size and dimension
Large image sizes can slow down a store’s website, which can negatively affect your search engine rankings and conversion rates.
Photos on a website should be optimized to achieve the optimal balance between clarity and file size to ensure quick page loads.
AMP implementation
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is a Google-backed initiative that uses an open standard to make mobile pages load quickly.
Despite not being a direct ranking factor, AMP improves the user experience and page speed for mobile users, ideally increasing user engagement.
10) Create backlinks
Backlinks are another ranking signal that Google uses to determine where your pages belong in the SERPs. The greater the number of backlinks from high-quality sites, the more authoritative your site becomes.
On average, the first result in Google SERP has 3.8 times more backlinks than the rest (2–10).
Building backlinks for your site need not be challenging. Guest posting on blogs related to your product or category is a simple and ethical method of link building. Simply send an email to the blog owners/influencers you’re interested in with three or more potential guest post ideas.
Another way is to create useful and shareable content. Wendy’s Lookbook produced a unique and comprehensive YouTube video on 25 Ways to Tie a Scarf. This 5-minute video has received over 45,495,940 views on YouTube to date.
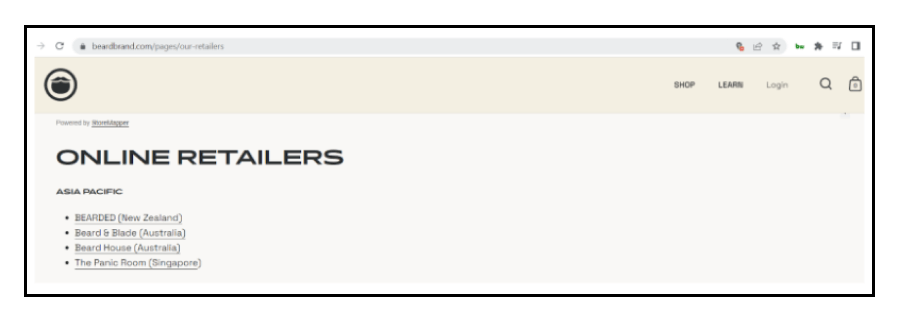
For many DTC umbrella brands that sell the products of another brand, it makes perfect sense to obtain a backlink from that brand’s website. Frequently, it is sufficient to send them a polite email requesting to be added to their directory of partners or retailers.
Beardbrand, for instance, lists all offline and online retailers of its beard oil, which not only helps those retailers sell more, but also improves their SEO by providing a backlink from their high-ranking domain:
11) Build informational content for your target audience
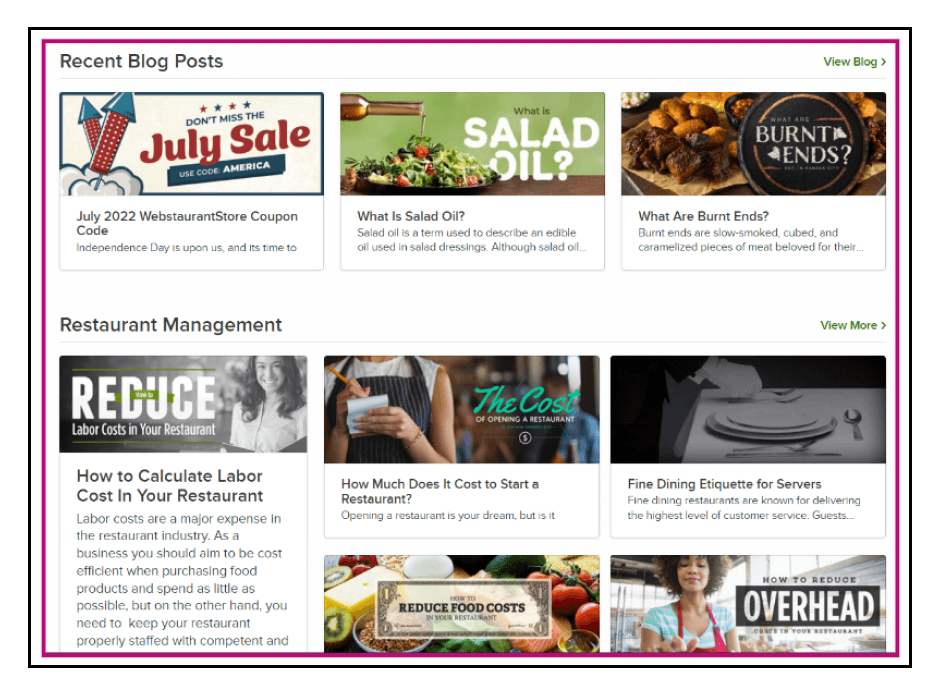
Many ecommerce brands apply this strategy to attract organic visitors. For instance, if you’re selling restaurant equipment, along with your online store, you can also have a blog and other resources wherein you cover different types of topics and how-tos around your products such as restaurant management, bar management, menu design, kitchen and cooking tips, and so many more. Something similar to this:
Use this SEO checklist
You may want to jump straight to increasing conversions. That’s the right mindset, but you’re a step ahead.
You have to get customers to your site before you can convert them on your offers. Beginning with ecommerce SEO sets you up for success.
Let’s take a relook at our checklist for ecommerce SEO:
- Analyze the keyword search volume, CPC, and user intent to use the right keywords.
- Remember to add LSI keywords.
- Conduct competitor research.
- Focus on homepage SEO.
- Simplify your site architecture.
- Optimize PDPs.
- Locate and fix 404 errors.
- Use mobile-first indexing and design.
- Reduce page load speed.
- Create backlinks.
- Build informational content for your target audience.
Continue to implement these SEO tips, and constantly seek to enhance UX and page speed.
You may also like
Essential resources for your success