This is the third part of our Geo-Experiments 101 series. The first part spoke about the basics of geo-experiments, why you should care, and how you can design your first geo-experiment. If you have not read it we encourage you to read part 1.
In the second part, we delved into deploying and managing a geo-test, market selection strategies, market size, and testing volume.
This is the final installment of the series where we will be talking about the analysis and reporting of geo-tests, how to measure incrementality and validation of your geo-tests, maximizing business impact, and explaining why continuous testing matters.
Let’s begin.
Analyzing and Reporting Geo-Tests
What’s the point of running tests if you cannot document your findings and analyze them for further improvements?
Analyzing and reporting your geo-tests is a pivotal phase of the entire process. However, there are different ways a team can approach this. We’ll navigate through the manual reporting for beginners, progress to semi-automated reporting for intermediaries, and finally, explore the efficiency of fully automated reporting for advanced marketers.
Manual reporting
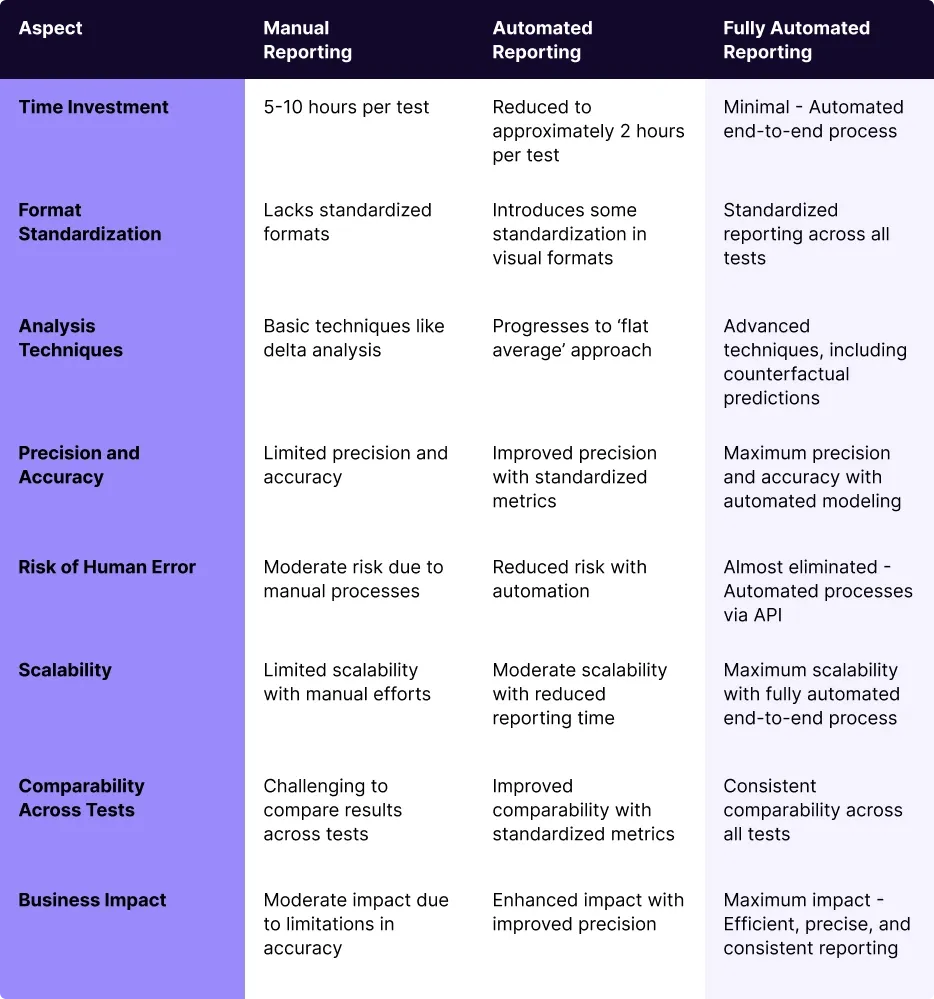
For beginners, manual reporting is often the starting point. This involves designing reports, aggregating sales data, selecting analysis techniques, and executing the analysis methodically. While this method is fundamental, it requires considerable time and effort, typically 5-10 hours for a basic test. The challenge intensifies as there’s no standardized reporting format, making it difficult to compare results across multiple tests and channels.
Despite its limitations, manual reporting provides a foundational understanding of the testing components. However, it’s essential to acknowledge its potential drawbacks, such as increased time investment and a lack of standardized comparison metrics.
Automated reporting
As you progress to an intermediate level, you’ll likely introduce automation into certain aspects of reporting. This alleviates some of the manual burdens, allowing for standardized visual formats and statistical diagnostics. Although the processes are still performed manually, the conclusion of automation reduces the overall reporting time, typically from 5 to 2 hours per test.
Intermediate-level testers often adopt techniques like a ‘flat average’ approach, comparing sales in test and control groups against a prior period. Additionally, confidence intervals might be applied for statistical precision, enhancing the reliability of results. While this level of automation streamlines reporting, it still requires hands-on execution and might lack the precision achieved in advanced practices.
Fully automated reporting
At the advanced level, you step into the realm of fully automated reporting. This sophisticated approach leverages big data analysis, machine learning, and predictive models based on control markets. The end-to-end process, from design to deployment and reporting, becomes automated, ensuring efficiency and precision.
Treatments to campaigns are trafficked automatically via API, significantly reducing the likelihood of human error. Transcript data seamlessly feeds back into an automated analysis framework, populating reports as the test progresses. Notably, reporting is based on a counterfactual prediction, offering precise confidence bounds for any tested result. This standardized approach ensures consistency and comparability across all tests.
Here’s a table summarizing the three reporting approaches:
Measuring Incrementality and Ensuring Validity in Geo Tests
Incrementality is the golden metric in geo testing, representing the lift in Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) attributed to your marketing efforts. It answers the fundamental question: How much of KPI ‘X’ resulted from my ads, as opposed to what would have occurred organically?
The journey from basic to advanced methods:
In the early stages, many opt for matched market tests, where similar geographies are treated differently to observe the impact. However, this method involves uncertainties and assumptions, making it less recommended.
Intermediate testers often employ Difference-in-Difference (DID) analysis, comparing trends in two markets to estimate the effect of ads. While more robust than matched markets, DID introduces complexities and assumptions.
The advanced, industry-standard method is predicted counterfactuals. This technique designates test markets, models synthetic untreated versions, and compares real observed behavior to the modeled versions. Unified Marketing measurement tools like Lifesight automate this complex process, optimizing market selection, model terms, and confidence intervals.
Ensuring validity: The guardian of trustworthy results
Validation is crucial to ensuring that your experimental setup was accurate and the observed results can be trusted. Here’s how you can validate your geo tests effectively:
1. Resampling and P-Values:
If you’re using DID, resampling can provide a distribution of your estimator, helping calculate a p-value. This statistic indicated the probability that observed results are not due to chance. However, this method has limitations.
2. Retroactive “A/A” tests:
With predicted counterfactuals, you can conduct retroactive “A/A” tests, modeling synthetic control for a period with observed untreated data. This validates the model’s accuracy and helps detect any artificial lift.
3. Confidence Intervals:
Fully automated platforms like Lifesight implement clear confidence intervals. Results falling outside these intervals are termed “statistically significant”, indicating low chances of occurring by chance.
As you venture into geo testing, calculating incrementality and validating results are the linchpins of reliable insights. Whether you’re adopting basic methods or embracing advanced predictive models, precision and confidence in your results set the stage for informed marketing decisions.
Maximizing Business Impact: Navigating Risks in Geo-Testing
Geo-testing, while a powerful tool, is not without its risks. The larger the test market, the greater the potential loss of sales during the testing period. Add to this the challenge of inconclusive results, contaminated data, and the significant investment of time and resources, and you’re navigating a complex landscape.
The traditional approach, especially at beginner and intermediate levels, often involves holding out a substantial portion of the country for testing. This can lead to a substantial volume of lost sales. The bigger the market size for testing, the higher the stakes.
Also, beginner and intermediate design and analysis techniques may yield results prone to contamination, noise, and lack of representativeness. Inconclusive or misleading results can leave marketers in a state of uncertainty, impacting their confidence in making significant media investment decisions.
Executing a testing practice that neither yields the volume of tests per year nor the accuracy of conclusive tests can also be a silent killer of time, effort, and resources. Brands might revert to less superior forms of media measurement, stalling progress and hindering strategic decision-making.
Advanced practices to the rescue
Advanced geo-testing practices shine as a beacon of efficiency, providing a roadmap to minimize these risks and amplify business impact.
1. Reducing market size with predicted counterfactuals:
The most sophisticated geo-testing involves predicted counterfactuals. By creating models based on trends in control markets, only 5-10% of markets need to be used in a treatment group. This drastic reduction in market size significantly decreases the risk of lost sales during testing.
2. Automated deployment for precision:
Fully automated testing platforms, like Lifesight, streamline the end-to-end process. Automated deployment via APIs ensure precision in trafficking treatments to campaigns, reducing the likelihood of human error and providing early visibility into test performance.
3. Efficient reporting and analysis:
Automated reporting and analysis further contribute to efficiency. Brands can leverage sophisticated analytical practices with standardized visual formats, ensuring precise results and freeing up time for strategic decision-making.
Why Continuous Testing Matters?
There are two ways to look at Geo-Testing: You can either use it just as a strategic advantage or make it the heartbeat of sustained growth and enhanced performance. The best brands usually do the latter. But there are reasons for that.
The power of ongoing insight
1. Adaptive decision-making:
Continuous testing allows brands to adapt swiftly to dynamic market changes. In a landscape where consumer behavior, trends, and competitive landscapes are in constant flux, the ability to make informed, adaptive decisions is a strategic advantage.
2. Iterative refinement:
Think of continuous testing as a refining process. Each test is a learning opportunity. Brands can refine their strategies, pinpoint what works best, and progressively enhance their approach. Iterative refinement is the heartbeat of sustainable growth.
3. Proactive issue identification:
Unforeseen issues can hamper the effectiveness of marketing strategies. Continuous testing acts as a proactive detective, identifying issues in real time. Brands can address challenges promptly, preventing potential setbacks.
4. Maximizing ROI:
We are already in a dynamic world where things change rapidly. Maintaining and maximizing ROI in such a setup is paramount but needs constant learning. Continuous testing allows brands to fine-tune their campaigns, optimizing for performance and ensuring that every marketing dollar spent contributes to the bottom line.
Concluding it
Since the series delved into the everything of geo-testing–from design to deployment to reporting, we wanted to also stress on some takeaways that can lead to sustainable growth and performance.
- Embrace change with confidence: Rather than being reactive, become proactive. Anticipate shifts and stay ahead of the curve.
- Build a culture of learning: Foster a mindset where every test is a lesson, and each lesson contributes to a collective pool of knowledge.
- Stay ahead in the competitive landscape: Consistently optimize your strategies. Ensure your brand is not just keeping pace but leading the charge.
- Elevate customer experience: Tailor your strategies to evolving customer needs, providing an elevated and personalized experience that resonates.
As we end the geo-testing series, we invite you to consider the impact of geo-testing on your marketing endeavors. Precision is not just a strategy; it’s a journey, and with each geo experiment, you refine your path to excellence.
With that being said, you can take your first step towards geo-testing by requesting for a personalized demo with Lifesight which offers fully automated geo-testing capabilities.
You may also like
Essential resources for your success